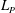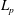13 results
GRADIENT ESTIMATES VIA TWO-POINT FUNCTIONS FOR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS UNDER RICCI FLOW
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 102 / Issue 2 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 319-330
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Variational Iteration Method for an Inverse Problem of Finding a Source Parameter
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2017, pp. 861-867
- Print publication:
- August 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the Fattorini criterion for approximate controllability and stabilizability of parabolic systems
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 20 / Issue 3 / July 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2014, pp. 924-956
- Print publication:
- July 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation
WEIGHTED
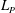 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}{L}_{{P}}$ SOLVABILITY FOR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS WITH PARTIALLY BMO COEFFICIENTS AND ITS APPLICATIONS
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}{L}_{{P}}$ SOLVABILITY FOR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS WITH PARTIALLY BMO COEFFICIENTS AND ITS APPLICATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 3 / June 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2014, pp. 396-428
- Print publication:
- June 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Exact null internal controllability for the heat equation on unbounded convex domains∗
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 January 2014, pp. 222-235
- Print publication:
- January 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alternating Direction Implicit Orthogonal Spline Collocation on Non-Rectangular Regions
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics / Volume 5 / Issue 4 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2015, pp. 461-476
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
A New Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Parabolic Equations with Discontinuous Coefficient
-
- Journal:
- Numerical Mathematics: Theory, Methods and Applications / Volume 6 / Issue 2 / May 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 May 2015, pp. 325-342
- Print publication:
- May 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Controllability properties for the one-dimensional Heatequation under multiplicative or nonnegative additive controls with local mobilesupport∗∗∗
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 18 / Issue 4 / October 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2012, pp. 1207-1224
- Print publication:
- October 2012
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimality conditions for semilinear parabolic equations withcontrols in leading term*
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2010, pp. 975-994
- Print publication:
- October 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
On regularization methods for the numerical solutionof paraboliccontrol problems with pointwisestate constraints
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 15 / Issue 2 / April 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2008, pp. 426-453
- Print publication:
- April 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Superreplication of Options on Several Underlying Assets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 42 / Issue 1 / March 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 27-38
- Print publication:
- March 2005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Optimal Control of Semilinear Parabolic Equations with State-Constraints of Bottleneck Type
-
- Journal:
- ESAIM: Control, Optimisation and Calculus of Variations / Volume 4 / 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2002, pp. 595-608
- Print publication:
- 1999
-
- Article
- Export citation
Boundedness of Solutions of Parabolic Equations With Anisotropic Growth Conditions
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 49 / Issue 4 / 01 August 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 798-809
- Print publication:
- 01 August 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation