The crystal structure and thermal expansion of the perovskite samarium cobalt oxide (SmCoO3) have been determined over the temperature range 295–1245 K by Rietveld analysis of X-ray powder diffraction data. Polycrystalline samples were prepared by a sol–gel synthesis route followed by high-temperature calcination in air. SmCoO3 is orthorhombic (Pnma) at all temperatures and is isostructural with GdFeO3. The structure was refined as a distortion mode of a parent 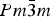 $ Pm{\bar 3}m $ structure. The thermal expansion was found to be non-linear and anisotropic, with maximum average linear thermal expansion coefficients of 34.0(3) × 10−6, 24.05(17) × 10−6, and 24.10(18) × 10−6 K−1 along the a-, b-, and c-axes, respectively, between 814 and 875 K.
$ Pm{\bar 3}m $ structure. The thermal expansion was found to be non-linear and anisotropic, with maximum average linear thermal expansion coefficients of 34.0(3) × 10−6, 24.05(17) × 10−6, and 24.10(18) × 10−6 K−1 along the a-, b-, and c-axes, respectively, between 814 and 875 K.