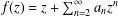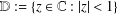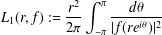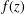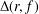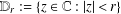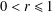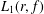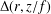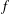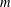For a normalized analytic function 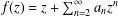 f(z)=z+\sum _{n=2}^{\infty }a_{n}z^{n} in the unit disk
f(z)=z+\sum _{n=2}^{\infty }a_{n}z^{n} in the unit disk 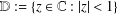 \mathbb{D}:=\{z\in \mathbb{C}:|z|<1\}, the estimate of the integral means
\mathbb{D}:=\{z\in \mathbb{C}:|z|<1\}, the estimate of the integral means
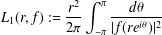 \begin{eqnarray}L_{1}(r,f):=\frac{r^{2}}{2{\it\pi}}\int _{-{\it\pi}}^{{\it\pi}}\frac{d{\it\theta}}{|f(re^{i{\it\theta}})|^{2}}\end{eqnarray}
\begin{eqnarray}L_{1}(r,f):=\frac{r^{2}}{2{\it\pi}}\int _{-{\it\pi}}^{{\it\pi}}\frac{d{\it\theta}}{|f(re^{i{\it\theta}})|^{2}}\end{eqnarray} is an important quantity for certain problems in fluid dynamics, especially when the functions
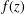 f(z)
f(z) are nonvanishing in the punctured unit disk
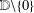 \mathbb{D}\setminus \{0\}
\mathbb{D}\setminus \{0\}. Let
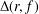 {\rm\Delta}(r,f)
{\rm\Delta}(r,f) denote the area of the image of the subdisk
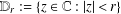 \mathbb{D}_{r}:=\{z\in \mathbb{C}:|z|<r\}
\mathbb{D}_{r}:=\{z\in \mathbb{C}:|z|<r\} under
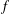 f
f, where
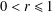 0<r\leq 1
0<r\leq 1. In this paper, we solve two extremal problems of finding the maximum value of
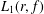 L_{1}(r,f)
L_{1}(r,f) and
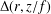 {\rm\Delta}(r,z/f)
{\rm\Delta}(r,z/f) as a function of
 r
r when
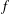 f
f belongs to the class of
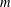 m
m-fold symmetric starlike functions of complex order defined by a subordination relation. One of the particular cases of the latter problem includes the solution to a conjecture of Yamashita, which was settled recently by Obradović
et al. [‘A proof of Yamashita’s conjecture on area integral’,
Comput. Methods Funct. Theory13 (2013), 479–492].