Open access
Contents
JFM Papers
Capturing the motion of a pair of elastic capsules in a shear flow: emergent nonlinear hydrodynamic ordering
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, A50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corrigendum
The joint effects of planetary
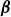 $\boldsymbol{\beta}$, topography and friction on baroclinic instability in a two-layer QG model – CORRIGENDUM
$\boldsymbol{\beta}$, topography and friction on baroclinic instability in a two-layer QG model – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, E1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JFM Papers
Buckling of a floating fluid layer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2026, A42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Passive drag reduction on a sphere using azimuthally spaced surface protrusions: effects of protrusion number at fixed coverage
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2026, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dissolution-driven transport in a rotating horizontal cylinder
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2026, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JFM Rapids
Unsteady aerodynamic theory and experiments of hovering membrane wings
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2026, R2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JFM Papers
Linear and nonlinear interactions between stationary cross-flow instabilities and a smooth surface hump
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2026, A43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of aspect ratio on the stability of rotating microchannel flows with superhydrophobic walls
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2026, A33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanism generating reverse buoyancy flux at the small scales of stably stratified turbulence
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2026, A35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of spanwise streamline curvature on a spatially developing boundary layer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2026, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The mechanism of laminar boundary layer vortex shedding noise generation of jet–wing interaction under the wing-in-ground effect
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2026, A29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Revisiting the validity of eddy viscosity models for predicting airflow over water waves
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Discrete vortex-based broadcast mode analysis for mitigation of dynamic stall
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Noise-generation mechanisms of a wing-tip vortex at moderate angle of attack
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Direct numerical simulations of non-coalescing floating bubbles: geometry and self-organisation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plane-marching PSE wavepacket models for perfectly expanded twin jets
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Role of acoustic metasurface in the nonlinear mode–mode interaction and breakdown of hypersonic boundary layer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The accelerated propagation of pulsed gravity currents
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laminar–turbulent patterns in plane Couette flow: influence of three-dimensional roughness
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turbulent flow over isolated forested hills of varying shape and steepness
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2026, A16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation