Article contents
DISTRIBUTED PROXIMAL-GRADIENT METHOD FOR CONVEX OPTIMIZATION WITH INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 November 2014
Abstract
We consider a distributed optimization problem over a multi-agent network, in which the sum of several local convex objective functions is minimized subject to global convex inequality constraints. We first transform the constrained optimization problem to an unconstrained one, using the exact penalty function method. Our transformed problem has a smaller number of variables and a simpler structure than the existing distributed primal–dual subgradient methods for constrained distributed optimization problems. Using the special structure of this problem, we then propose a distributed proximal-gradient algorithm over a time-changing connectivity network, and establish a convergence rate depending on the number of iterations, the network topology and the number of agents. Although the transformed problem is nonsmooth by nature, our method can still achieve a convergence rate, 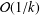 ${\mathcal{O}}(1/k)$, after
${\mathcal{O}}(1/k)$, after 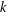 $k$ iterations, which is faster than the rate,
$k$ iterations, which is faster than the rate, 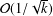 ${\mathcal{O}}(1/\sqrt{k})$, of existing distributed subgradient-based methods. Simulation experiments on a distributed state estimation problem illustrate the excellent performance of our proposed method.
${\mathcal{O}}(1/\sqrt{k})$, of existing distributed subgradient-based methods. Simulation experiments on a distributed state estimation problem illustrate the excellent performance of our proposed method.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © 2014 Australian Mathematical Society
References
- 4
- Cited by

