Case report
A 17-year-old, non-hypertensive female was admitted to our cardiology centre with frequent malignant arrhythmias leading to syncopal attacks. She had previously visited another hospital with the same presentation. Resuscitation was successfully achieved after electric cardioversions and cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Cardiac monitor tracing and 24-hour Holter monitoring revealed frequent torsades de pointes ventricular tachycardia, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator was implanted for primary prevention, but subsequently the patient experienced repeated implantable cardioverter defibrillator shocks and syncopal episodes. She had no specific family or personal history. Her coronary arteries were normal on coronary angiography.
On admission to our hospital, cardiac auscultation revealed a holosystolic murmur with punctum maximum at the apex. The patient was normotensive and her transthoracic echocardiography revealed severe left ventricular dysfunction, contractile abnormality of severe diffuse hypokinesis and decreased left ventricular ejection fraction of 28%. Laboratory results showed a significant elevation of N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide levels (5648 pg/mL, reference range: 0–110 pg/mL). Plasma test showed high epinephrine level of 420 mg/24 h (reference range: 0–100 mg/24 h) and high norepinephrine level of 8141 mg/24 h (reference range: 0–600 mg/24 h). Similar results were obtained in urinalysis. Epinephrine level in urine was 38.7 mg/24 h (reference range: 0–20 mg/24 h) and norepinephrine level was 340 mg/24 h (reference range: 0–0 mg/24 h). A mass was found in the adrenal gland by a high-resolution CT scan (Fig. 1). Hence, the patient underwent surgical robotic left adrenalectomy. Histological and immunohistochemical analyses confirmed the initial diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. The levels of norepinephrine and catecholamine excretion in the plasma and urine decreased to normal range after surgery. Echocardiography showed significant recovery of cardiac function.
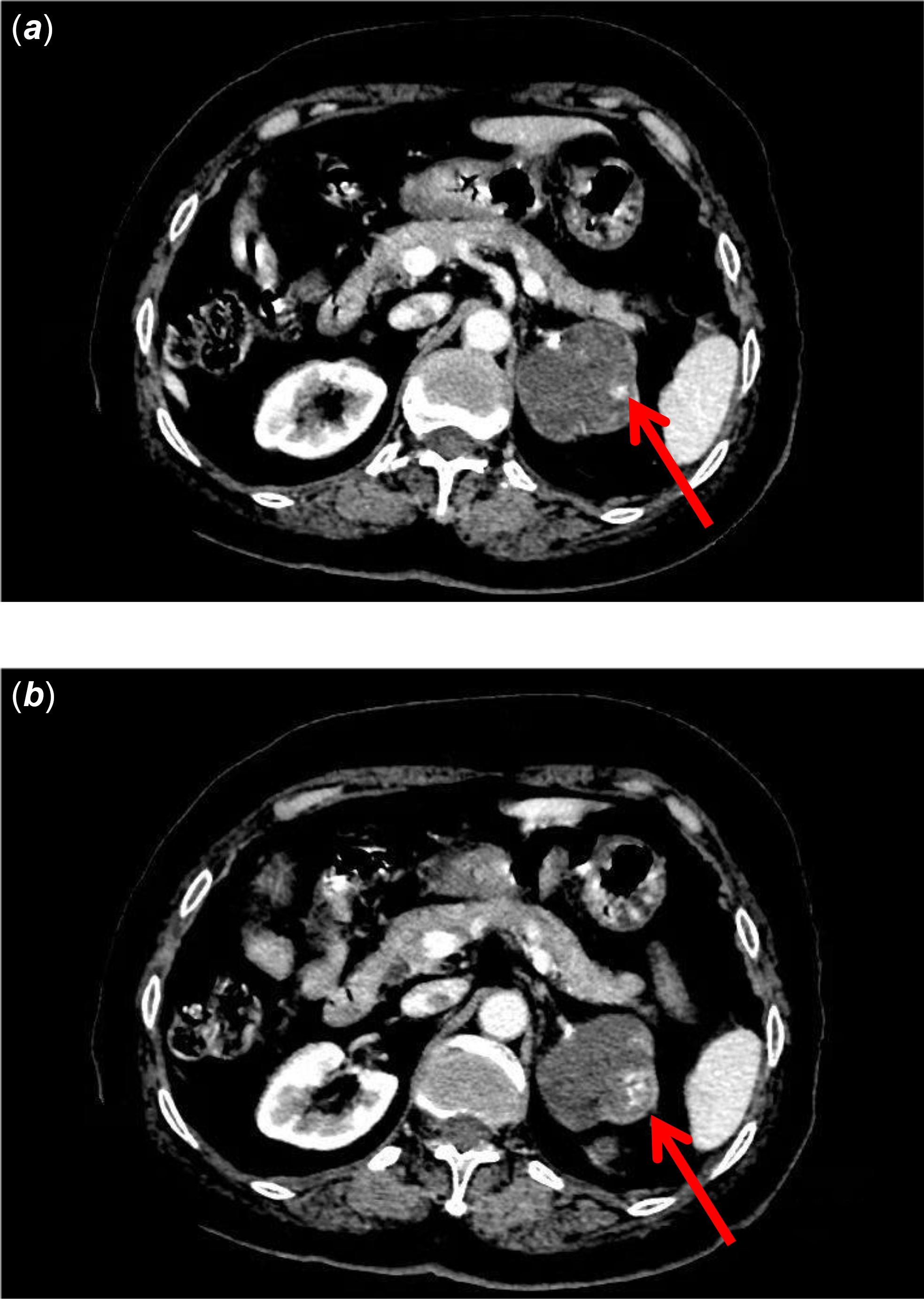
Figure 1. CT scan ( a ) showed an approximately round mass in the left adrenal gland, with a clear boundary between peripheral tissues, a smooth edge, and inhomogeneous enhancement ( b ) on enhanced scans.
The patient remained asymptomatic, and no ventricular arrhythmias were observed in the implantable cardioverter defibrillator memory 5 years after the surgery. The patient was discharged with no further medications but was advised regular outpatient visits.
Discussion
Pheochromocytoma is a rare adrenal tumour. In extremely rare cases, it can cause cardiac dysfunction secondary to adrenergic stimulation from catecholamine surges, including fatal arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Identifying the biochemical phenotype of a pheochromocytoma is the first step in evaluating catecholamine-induced tachyarrhythmias and dysregulation of blood pressure. Reference Jenča, Kubánek and Kudla1–Reference Lanot, Adda, Roubille and Akodad3 Catecholamines bind with different affinities to adrenoceptors in multiple organs, including the heart and vasculature, leading to tachyarrhythmias and blood pressure changes. Reference Kaneto, Kamei and Tatsumi4–Reference Gauvin, Klyachman and Grewal5 Although cardiac β1-adrenoceptor stimulation by both norepinephrine and epinephrine causes tachyarrhythmias, the effect on the vasculature is determined by the distribution and affinities. Owing to its higher affinity for ß1 compared to α1-adrenoceptors, epinephrine has a tendency to cause tachyarrhythmias instead of hypertension, which is in contrast to the action of norepinephrine. Reference Gauvin, Klyachman and Grewal5 Our patient did not experience hypertension despite a significant elevation of norepinephrine in plasma and urine tests. It is possible that undetected transient hypertension crisis may have induced cardiac failure and dilatation. The subcutaneous defibrillator is primarily recommended to prevent episodes of cardiac arrest, recurrent syncope, or malignant arrhythmias. Although implantable cardioverter defibrillator is a logical option for management, Reference Christina, Peter, Bernhard and Gerhard6 multiple device therapy is associated with high burden of shocks, thereby decreasing the quality of life, and recurrent adrenaline-provoking shocks, inappropriate shocks by complex atrial, and ventricular arrhythmias can worsen ventricular systolic function. Reference Kaneto, Kamei and Tatsumi4.Reference Christina, Peter, Bernhard and Gerhard6,Reference Li, Huang, Jiang and Chen7,Reference Molaei, Abarzadeh-Bairami and Sadat-Ebrahimi8
It is vital to correctly identify and diagnose the cause of malignant tachyarrhythmias in order to administer appropriate treatment. Clinicians should meticulously search for pheochromocytoma before considering implantable cardioverter defibrillator, as its detection and removal will be curative, and avoid unnecessary device implantation and associated complications. It is also important to note that pheochromocytoma is not always accompanied by hypertension.
Acknowledgements
None.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interest
None.




