No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
DT INVARIANTS FROM VERTEX ALGEBRAS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 September 2024
Abstract
We obtain a new interpretation of the cohomological Hall algebra 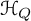 $\mathcal {H}_Q$ of a symmetric quiver Q in the context of the theory of vertex algebras. Namely, we show that the graded dual of
$\mathcal {H}_Q$ of a symmetric quiver Q in the context of the theory of vertex algebras. Namely, we show that the graded dual of 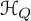 $\mathcal {H}_Q$ is naturally identified with the underlying vector space of the principal free vertex algebra associated to the Euler form of Q. Properties of that vertex algebra are shown to account for the key results about
$\mathcal {H}_Q$ is naturally identified with the underlying vector space of the principal free vertex algebra associated to the Euler form of Q. Properties of that vertex algebra are shown to account for the key results about 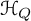 $\mathcal {H}_Q$. In particular, it has a natural structure of a vertex bialgebra, leading to a new interpretation of the product of
$\mathcal {H}_Q$. In particular, it has a natural structure of a vertex bialgebra, leading to a new interpretation of the product of 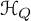 $\mathcal {H}_Q$. Moreover, it is isomorphic to the universal enveloping vertex algebra of a certain vertex Lie algebra, which leads to a new interpretation of Donaldson–Thomas invariants of Q (and, in particular, re-proves their positivity). Finally, it is possible to use that vertex algebra to give a new interpretation of CoHA modules made of cohomologies of non-commutative Hilbert schemes.
$\mathcal {H}_Q$. Moreover, it is isomorphic to the universal enveloping vertex algebra of a certain vertex Lie algebra, which leads to a new interpretation of Donaldson–Thomas invariants of Q (and, in particular, re-proves their positivity). Finally, it is possible to use that vertex algebra to give a new interpretation of CoHA modules made of cohomologies of non-commutative Hilbert schemes.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 24 , Issue 1 , January 2025 , pp. 291 - 339
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press


