Article contents
Summing spectra in gamma spectrometry for improving detection of low-level radionuclides in aerosol samples
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 June 2005
Abstract
In the frame of IRSN's French radioactivity observatory, aerosol samples are collected in a ten-days basis in different locations and measured by gamma spectrometry. For some studies, it is necessary to have the average of a radionuclide in aerosol samples, i.e. monthly or annually. Gamma spectrometry measurement of artificial radionuclides such as 137Cs is becoming more difficult due to decreasing radioactivity levels. Individual measurements are sometimes below the minimum detectable activity (MDA) even when low-background measurement procedures are used. In these cases, how can a MDA in an average computation be taken into account? In order to acquire this mean value, the analysis can be performed on the annual spectrum corresponding to a running sum of each individual spectrum. As for the sample, the summing is applied for the background spectrum. In this way, the 137Cs concentration in aerosols corresponding to the annual mean value is obtained. For aerosols collected in La Reunion, a mean concentration of $0.029 \pm 0.010 \mathrm{\mu}$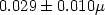 Bq.$\textrm{m}^{-3}$
Bq.$\textrm{m}^{-3}$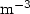 for 137Cs is obtained, when 25 measurement results on 26 samples are below the MDA. For radionuclides always detected, a good agreement between summing spectrum results and computed mean value is observed.
for 137Cs is obtained, when 25 measurement results on 26 samples are below the MDA. For radionuclides always detected, a good agreement between summing spectrum results and computed mean value is observed.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2005
- 2
- Cited by

