The presence of fat in the small intestine and its subsequent digestion into free fatty acids slows gastric emptying, stimulates gastrointestinal hormone release and suppresses appetite and energy intake(Reference Little, Russo and Meyer1). Lipids vary substantially in fatty acid composition, chain length and degree of saturation so may not all elicit the same response(Reference McLaughlin2). The differential effects of long chain fatty acids on energy intake and body weight are not comprehensively understood(Reference Li, Huang and Xie3). This study aimed to investigate the effect of omega-3-rich and -poor emulsions on subsequent energy intake.
A controlled, crossover intervention using normal and overweight males (n=18) was conducted to examine 24-hr energy intake after two different 45% oil-in-water emulsions of (docosahexaenoic acid) DHA and oleic acid (OA), compared to no treatment (NT). Energy intake was 12,097 kJ after NT, 9,912 kJ after OA and 8,539 kJ after DHA. The difference between DHA and NT was statistically significant (Table 1).
A double-blind, randomised controlled parallel trial was conducted to examine the effects of DHA consumption over twelve weeks compared to OA on energy intake and body weight. Overweight and obese females (n=40) consumed either emulsion before lunch and evening meal for twelve weeks. Mean body weight (kg) was significantly reduced by 3.5% in the DHA group compared to 1.1% in the OA group (P=.037). Body mass index (kg/m2) was significantly reduced by 3.9% in the DHA group compared to 1.9% in the OA group (P=.032). There was no effect of treatment on body composition. Differential reduction in energy contribution between macronutrient groups was noted (Table 2).
Table 1. Results of the acute feeding experiment
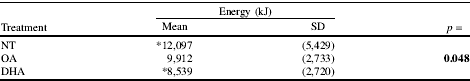
* Post hoc tests indicate mean energy intake for NT was significantly (P=.039) different from DHA.
Table 2. Results of the 12 week intervention presented as change from baseline
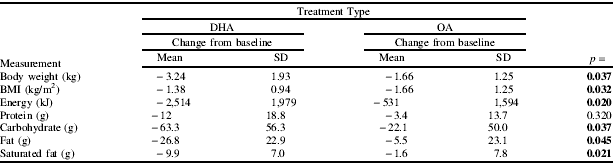
In two human feeding studies, DHA consumption significantly reduced total daily energy intake in comparison with isocaloric dosing of a non-omega-3-rich preparation. These data suggest that position of desaturation may play a role in the regulation of appetite by lipids.




