Refine search
Actions for selected content:
1 results
An Essential Extension of the Finite-Energy Condition for Extended Runge-Kutta-Nyström Integrators when Applied to Nonlinear Wave Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Communications in Computational Physics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2017, pp. 742-764
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
 , where
, where 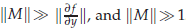 . The highly oscillatory system is due to the semi-discretisation of conservative, or dissipative, nonlinear wave equations. The structure of such a matrix
. The highly oscillatory system is due to the semi-discretisation of conservative, or dissipative, nonlinear wave equations. The structure of such a matrix 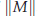 . Since stepsizes are not restricted by frequencies of
. Since stepsizes are not restricted by frequencies of 