1. Introduction
An irrotational motion of incompressible two-dimensional surface water waves can be fully described by means of evolution equations for two canonical variables in one spatial coordinate. This formalism was originated by Zakharov (Reference Zakharov1968) in the context of the stability of travelling periodic waves.
One approach to developing this formalism systematically is based on the Dirichlet-to-Neumann (D-N) operator (Craig & Sulem Reference Craig and Sulem1993). The two nonlinear evolution equations closed with the D-N operator have been studied in many works on water waves, including the recent study of modulational instability of travelling periodic waves (Berti, Maspero & Ventura Reference Berti, Maspero and Ventura2022). See also Creedon & Deconinck (Reference Creedon and Deconinck2023), Hur & Yang (Reference Hur and Yang2023) and Nguyen & Strauss (Reference Nguyen and Strauss2023) for other recent works where three more methods have been explored in the same context.
Another approach to obtaining a closed system of two nonlinear evolution equations for water waves is based on a conformal transformation which maps the fluid domain with a variable surface profile to a fixed rectangular domain. This formalism was introduced in Babenko (Reference Babenko1987) and Tanveer (Reference Tanveer1991) and has been explored in the context of travelling periodic waves in Dyachenko et al. (Reference Dyachenko, Kuznetsov, Spector and Zakharov1996), Zakharov & Dyachenko (Reference Zakharov and Dyachenko1996), Choi & Camassa (Reference Choi and Camassa1999) and more recently in Dyachenko, Lushnikov & Korotkevich (Reference Dyachenko, Lushnikov and Korotkevich2016), Dyachenko & Semenova (Reference Dyachenko and Semenova2023a,Reference Dyachenko and Semenovab), Korotkevich et al. (Reference Korotkevich, Lushnikov, Semenova and Dyachenko2023) and Lushnikov, Dyachenko & Silantyev (Reference Lushnikov, Dyachenko and Silantyev2017). Our work contributes to the analysis of the nonlinear evolution equations obtained in the latter approach.
The approach based on conformal transformations has been used to tackle many mathematical problems related to water waves such as the existence of standing waves (Wilkening Reference Wilkening2020, Reference Wilkening2021) and bifurcations of quasi-periodic wave solutions from the standing periodic waves (Wilkening & Zhao Reference Wilkening and Zhao2021, Reference Wilkening and Zhao2023a,Reference Wilkening and Zhaob). Holomorphic coordinates were used for analysis of the well posedness of the water wave equations (Hunter, Ifrim & Tataru Reference Hunter, Ifrim and Tataru2016; Harrop–Griffiths, Ifrim & Tataru Reference Harrop–Griffiths, Ifrim and Tataru2017). The particular problem addressed in our work is the coexistence of smooth and peaked travelling periodic waves for different intervals of wave speeds as well as the linear stability of waves with smooth profiles.
1.1. A new model equation
The purpose of this paper is to introduce a new model equation which shares the same solutions as the travelling wave reduction of Euler's equations in Babenko (Reference Babenko1987) but simplifies the time evolution and, particularly, the linear stability analysis of the travelling periodic waves. This model equation can be written in the following non-local form:
where ![]() $\eta = \eta (u,t) \in \mathbb {R}$ is the surface elevation in the reference frame moving with the constant wave speed
$\eta = \eta (u,t) \in \mathbb {R}$ is the surface elevation in the reference frame moving with the constant wave speed ![]() $c > 0$,
$c > 0$, ![]() $t \in \mathbb {R}$ is time and
$t \in \mathbb {R}$ is time and ![]() $u$ is the spatial coordinate defined on the periodic domain
$u$ is the spatial coordinate defined on the periodic domain ![]() $\mathbb {T} = \mathbb {R} \backslash (2{\rm \pi} \mathbb {Z})$. The spatial coordinate
$\mathbb {T} = \mathbb {R} \backslash (2{\rm \pi} \mathbb {Z})$. The spatial coordinate ![]() $u$ arises after the conformal transformation of the fluid domain with variable surface elevation
$u$ arises after the conformal transformation of the fluid domain with variable surface elevation ![]() $\eta$ to a rectangle
$\eta$ to a rectangle ![]() $[-{\rm \pi},{\rm \pi}] \times [-h,0]$, where
$[-{\rm \pi},{\rm \pi}] \times [-h,0]$, where ![]() $h > 0$ is the fluid depth. The linear skew–adjoint operator
$h > 0$ is the fluid depth. The linear skew–adjoint operator ![]() $T_h^{-1}$ in
$T_h^{-1}$ in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
whereas the linear, self-adjoint, positive operator ![]() $K_h = T_h^{-1} \partial _u$ in
$K_h = T_h^{-1} \partial _u$ in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
Appendix A explains how the non-local evolution equation (1.1) arises in the context of the original Euler's equations.
Let us obtain the conserved quantities for the non-local model (1.1). Taking the mean value of (1.1), we get the constraint
which represents the zero-mean constraint for the surface elevation ![]() $\eta$ in the physical spatial coordinate. Furthermore, differentiating (1.1) in
$\eta$ in the physical spatial coordinate. Furthermore, differentiating (1.1) in ![]() $u$, multiplying by
$u$, multiplying by ![]() $\eta$ and integrating over the period of
$\eta$ and integrating over the period of ![]() $\mathbb {T}$ yields
$\mathbb {T}$ yields
 \begin{align} c \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} t} \oint \eta K_h \eta\,{\rm d} u &= \oint (c^2 \eta K_h \eta_u - \eta \eta_u - \eta \eta_u K_h \eta - \eta^2 K_h \eta_u - \eta K_h \eta \eta_u )\,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &= \oint \partial_u \left(\tfrac{1}{2} c^2 \eta K_h \eta - \tfrac{1}{2} \eta^2 - \eta^2 K_h \eta \right) {\rm d} u = 0, \end{align}
\begin{align} c \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} t} \oint \eta K_h \eta\,{\rm d} u &= \oint (c^2 \eta K_h \eta_u - \eta \eta_u - \eta \eta_u K_h \eta - \eta^2 K_h \eta_u - \eta K_h \eta \eta_u )\,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &= \oint \partial_u \left(\tfrac{1}{2} c^2 \eta K_h \eta - \tfrac{1}{2} \eta^2 - \eta^2 K_h \eta \right) {\rm d} u = 0, \end{align}
where we have used self-adjointness of ![]() $K_h$ in
$K_h$ in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ for every solution with
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ for every solution with ![]() $\eta, \eta _u, \eta \eta _u$ in the domain of
$\eta, \eta _u, \eta \eta _u$ in the domain of ![]() $K_h$. It follows from (1.4) and (1.5) that the non-local evolution equation (1.1) admits two conserved quantities
$K_h$. It follows from (1.4) and (1.5) that the non-local evolution equation (1.1) admits two conserved quantities
In addition, the evolution equation (1.1) can be written in the Hamiltonian form
where ![]() $\varLambda _c(\eta )$ is the action related to the conserved energy of the fluid. Critical points of
$\varLambda _c(\eta )$ is the action related to the conserved energy of the fluid. Critical points of ![]() $\varLambda _c$ in the corresponding energy space satisfy the Euler–Lagrange equation
$\varLambda _c$ in the corresponding energy space satisfy the Euler–Lagrange equation
which is known as Babenko's equation because it coincides with the travelling wave reduction of Euler's equations after the conformal transformation (Babenko Reference Babenko1987). In the context of the evolution equation (1.1) with ![]() $u$ defined in the reference frame moving with the wave speed
$u$ defined in the reference frame moving with the wave speed ![]() $c$, solutions of (1.8) correspond to the time-independent solutions of (1.1).
$c$, solutions of (1.8) correspond to the time-independent solutions of (1.1).
1.2. Local model and main results
In the deep water limit (![]() $h \to \infty$), we have from (1.2) and (1.3) that
$h \to \infty$), we have from (1.2) and (1.3) that
where ![]() $\mathcal {H}$ is the periodic Hilbert transform defined by the Fourier symbol
$\mathcal {H}$ is the periodic Hilbert transform defined by the Fourier symbol
This work explores the shallow water limit (![]() $h \to 0$), when we replace
$h \to 0$), when we replace ![]() $T_h^{-1}$ and
$T_h^{-1}$ and ![]() $K_h$ by
$K_h$ by ![]() $-\partial _u$ and
$-\partial _u$ and ![]() $-\partial _u^2$, respectively. In other words, we study herein the local evolution equation
$-\partial _u^2$, respectively. In other words, we study herein the local evolution equation
Appendix B describes how the local model (1.11) arises from ![]() $T_h^{-1}$ and
$T_h^{-1}$ and ![]() $K_h$ as
$K_h$ as ![]() $h \to 0$ and compares it with other phenomenological models for fluid dynamics.
$h \to 0$ and compares it with other phenomenological models for fluid dynamics.
It is important to emphasize that (1.11) is not the asymptotic reduction of (1.1) as ![]() $h \to 0$ but rather a toy model to understand the existence and linear stability of travelling periodic waves in the shallow water limit.
$h \to 0$ but rather a toy model to understand the existence and linear stability of travelling periodic waves in the shallow water limit.
The local equation (1.11) without the last term was derived in Hunter & Saxton (Reference Hunter and Saxton1991) in a different (geometric) context and has been referred to as the Hunter–Saxton equation (Hunter & Zheng Reference Hunter and Zheng1994). The same equation (1.11) with the last term was also discussed in Alber et al. (Reference Alber, Camassa, Holm and Marsden1995, Reference Alber, Camassa, Fedorov, Holm and Marsden1999) in connection to the high-frequency limit of the Camassa–Holm equation, one of the toy models for the physics of fluids with smooth and peaked waves. Integrability of (1.11) was established in Hone, Novikov & Wang (Reference Hone, Novikov and Wang2018) together with other peaked wave equations such as the reduced Ostrovsky and short-pulse equations. Some travelling wave solutions of this and similar equations were studied with Hirota's bilinear method in Matsuno (Reference Matsuno2020).
Next, we discuss the time evolution and the conserved quantities for the local model (1.11). Taking the mean value of (1.11) for smooth ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions and integrating by parts yields the constraint
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions and integrating by parts yields the constraint
which corresponds to (1.4) also after integration by parts. Let ![]() $\varPi _0 : L^2(\mathbb {T}) \rightarrow L^2(\mathbb {T}) |_{\{1\}^T}$ be a projection operator to the periodic functions with zero mean. The evolution equation (1.11) can be written in the form
$\varPi _0 : L^2(\mathbb {T}) \rightarrow L^2(\mathbb {T}) |_{\{1\}^T}$ be a projection operator to the periodic functions with zero mean. The evolution equation (1.11) can be written in the form
where ![]() $\varPi _0 \partial _u^{-1} \varPi _0$ is uniquely defined on the zero-mean functions in
$\varPi _0 \partial _u^{-1} \varPi _0$ is uniquely defined on the zero-mean functions in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ with the zero-mean constraint. The evolution equation (1.13) is a non-local version of the inviscid Burgers equation. The initial-value problem for the inviscid Burgers equation is locally well posed in
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ with the zero-mean constraint. The evolution equation (1.13) is a non-local version of the inviscid Burgers equation. The initial-value problem for the inviscid Burgers equation is locally well posed in ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$. Since the mapping
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$. Since the mapping
is bounded on every bounded subset, there exists a unique local solution of the evolution equation (1.13) for every initial data in ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$.
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$.
To get the conserved quantities, we multiply (1.11) by ![]() $\partial _u \eta$ and integrate over the period for smooth
$\partial _u \eta$ and integrate over the period for smooth ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions ![]() $\eta$. This implies the conservation of
$\eta$. This implies the conservation of
and, in view of the constraint (1.12), the conservation of
The conserved quantities (1.15) and (1.16) correspond to (1.6a,b). Furthermore, similar to (1.7), we can write (1.13) in the Hamiltonian form
where ![]() $H$ is the third conserved quantity given by
$H$ is the third conserved quantity given by
The existence of travelling periodic waves in the local model (1.11) is defined by the second-order equation
where ![]() $\eta = \eta (u)$ is the
$\eta = \eta (u)$ is the ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic wave profile satisfying the constraint (1.12). The linear stability of the travelling wave with the profile
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic wave profile satisfying the constraint (1.12). The linear stability of the travelling wave with the profile ![]() $\eta$ is defined by the linearized equation
$\eta$ is defined by the linearized equation
where ![]() $\hat {\eta } = \hat {\eta }(u,t)$ is the perturbation to the travelling wave with the profile
$\hat {\eta } = \hat {\eta }(u,t)$ is the perturbation to the travelling wave with the profile ![]() $\eta = \eta (u)$ satisfying the orthogonality condition
$\eta = \eta (u)$ satisfying the orthogonality condition ![]() $\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ with the standard inner product in
$\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ with the standard inner product in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$. The orthogonality condition
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$. The orthogonality condition ![]() $\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ follows by expanding the nonlinear constraint (1.12) near
$\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ follows by expanding the nonlinear constraint (1.12) near ![]() $\eta$.
$\eta$.
The following two theorems describe the main results of this work. Our results are formulated for the single-lobe periodic solutions with an even profile ![]() $\eta$ which possesses a single maximum on
$\eta$ which possesses a single maximum on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$ placed at
$\mathbb {T}$ placed at ![]() $u = 0$. Such single-lobe periodic solutions are often referred to as Stokes waves.
$u = 0$. Such single-lobe periodic solutions are often referred to as Stokes waves.
Theorem 1.1 There exist ![]() $c_* := {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$ and
$c_* := {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$ and ![]() $c_{\infty } \in (c_*,\infty )$ such that the stationary equation (1.19) admits a unique single-lobe solution with the profile
$c_{\infty } \in (c_*,\infty )$ such that the stationary equation (1.19) admits a unique single-lobe solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ for every
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ for every ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ such that
$c \in (1,c_*)$ such that
and a single-lobe solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^0_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ for every
$\eta \in C^0_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ for every ![]() $c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$ satisfying
$c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$ satisfying
for some constant ![]() $A(c) > 0$. At
$A(c) > 0$. At ![]() $c = c_*$, there exists a unique single-lobe solution with the profile
$c = c_*$, there exists a unique single-lobe solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^0_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ given explicitly as
$\eta \in C^0_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ given explicitly as
and extended as a ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic function on
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic function on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$.
$\mathbb {T}$.
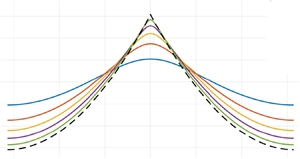
Remark 1.1 Figure 1 shows profiles of the periodic waves of Theorem 1.1. The profiles were obtained numerically by using solutions of the second-order equation (1.19).

Figure 1. Profiles in the family of smooth periodic waves (a) and singular periodic waves (b) vs ![]() $u$ for different values of wave speeds
$u$ for different values of wave speeds ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ and
$c \in (1,c_*)$ and ![]() $c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$, respectively. The dashed line shows the profile of the peaked periodic wave (1.23).
$c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$, respectively. The dashed line shows the profile of the peaked periodic wave (1.23).
Remark 1.2 There exists another single-lobe solution with the singular behaviour (1.22) for every ![]() $c \in (0,c_{\infty })$ which is not included in the statement of Theorem 1.1 as it does not bifurcate from the zero solution as
$c \in (0,c_{\infty })$ which is not included in the statement of Theorem 1.1 as it does not bifurcate from the zero solution as ![]() $c \to 1$ compared with (1.21). See figure 2 for the bifurcation diagram of all single-lobe solutions of (1.19).
$c \to 1$ compared with (1.21). See figure 2 for the bifurcation diagram of all single-lobe solutions of (1.19).

Figure 2. Dependence of ![]() $E := \| \eta \|_{L^{\infty }}$ vs wave speed
$E := \| \eta \|_{L^{\infty }}$ vs wave speed ![]() $c$ for periodic solutions of (1.19). The smooth solutions of Theorem 1.1 exist between the black dots. The singular solutions of Theorem 1.1 exist between the rightmost black and red dots. The singular solutions which are not included in the statement of Theorem 1.1 exist between the red dots.
$c$ for periodic solutions of (1.19). The smooth solutions of Theorem 1.1 exist between the black dots. The singular solutions of Theorem 1.1 exist between the rightmost black and red dots. The singular solutions which are not included in the statement of Theorem 1.1 exist between the red dots.
Remark 1.3 The special solution (1.23) has a peaked profile with a finite jump of the first derivative. It is usually referred to as the peaked periodic wave. Such peaked periodic waves are commonly known in other fluid models such as the reduced Ostrovsky equation (Geyer & Pelinovsky Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2019, Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2020; Bruell & Dhara Reference Bruell and Dhara2021), the Camassa–Holm equation (Madiyeva & Pelinovsky Reference Madiyeva and Pelinovsky2021) and the Degasperis–Procesi equation (Geyer & Pelinovsky Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2024).
Remark 1.4 The singular behaviour (1.22) corresponds to the singularity of the limiting Stokes wave with a ![]() $120^{\rm o}$ angle in the physical coordinate after the conformal transformation. The behaviour was rigorously proven for the original Euler's equation in Amick, Fraenkel & Toland (Reference Amick, Fraenkel and Toland1982), Plotnikov (Reference Plotnikov2002) and Toland (Reference Toland1978), with many asymptotic results known in the literature (see Lushnikov (Reference Lushnikov2016) and references therein). Note that
$120^{\rm o}$ angle in the physical coordinate after the conformal transformation. The behaviour was rigorously proven for the original Euler's equation in Amick, Fraenkel & Toland (Reference Amick, Fraenkel and Toland1982), Plotnikov (Reference Plotnikov2002) and Toland (Reference Toland1978), with many asymptotic results known in the literature (see Lushnikov (Reference Lushnikov2016) and references therein). Note that
holds for every limiting Stokes wave for which the horizontal velocity at the wave height coincides with the wave speed ![]() $c$, see the second equation in system (A3) of Appendix A.
$c$, see the second equation in system (A3) of Appendix A.
Theorem 1.2 Consider the unique single-lobe solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ in Theorem 1.1 for
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ in Theorem 1.1 for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$. For every initial data
$c \in (1,c_*)$. For every initial data ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0 \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ satisfying
$\hat {\eta }_0 \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ satisfying
there exists a unique solution ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation ( 1.20 a,b) with
$\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation ( 1.20 a,b) with ![]() $\hat {\eta } |_{t = 0} = \hat {\eta }_0$ and a unique
$\hat {\eta } |_{t = 0} = \hat {\eta }_0$ and a unique ![]() $a \in C^1(\mathbb {R},\mathbb {R})$ such that
$a \in C^1(\mathbb {R},\mathbb {R})$ such that
where ![]() $C > 0$ is independent of
$C > 0$ is independent of ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0$.
$\hat {\eta }_0$.
Remark 1.5 Constraints (1.25a,b) are preserved in the time evolution of the linearized equation (1.20a,b) because they are linearizations of the conserved quantities (1.15) and (1.16). In view of the constraint ![]() $\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ imposed on solutions of the linearized equation (1.20a,b), only one constraint in (1.25a,b) is linearly independent. Imposing
$\langle 1 - 2 \eta '', \hat {\eta } \rangle = 0$ imposed on solutions of the linearized equation (1.20a,b), only one constraint in (1.25a,b) is linearly independent. Imposing ![]() $\langle \eta '', \hat {\eta }_0 \rangle = 0$ is equivalent to the requirement that the perturbation
$\langle \eta '', \hat {\eta }_0 \rangle = 0$ is equivalent to the requirement that the perturbation ![]() $\hat {\eta }$ does not change the conserved quantity
$\hat {\eta }$ does not change the conserved quantity ![]() $Q$ in (1.15) up to the linear approximation. The bound (1.26a,b) expresses the concept of linear orbital stability of the orbit
$Q$ in (1.15) up to the linear approximation. The bound (1.26a,b) expresses the concept of linear orbital stability of the orbit ![]() $\{ \eta ({\cdot } + \mathfrak {u}) \}_{\mathfrak {u} \in \mathbb {T}}$ of the travelling periodic wave with the profile
$\{ \eta ({\cdot } + \mathfrak {u}) \}_{\mathfrak {u} \in \mathbb {T}}$ of the travelling periodic wave with the profile ![]() $\eta$.
$\eta$.
Remark 1.6 The linear orbital stability of Theorem 1.2 implies spectral stability of the travelling periodic wave in the sense that the spectrum of the associated linearized operator ![]() $\partial _u^{-1} \mathcal {L}$ in
$\partial _u^{-1} \mathcal {L}$ in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ belongs to
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ belongs to ![]() $i \mathbb {R}$. It is also worthwhile to point out that an eigenfunction
$i \mathbb {R}$. It is also worthwhile to point out that an eigenfunction ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0$ of the spectral stability problem
$\hat {\eta }_0$ of the spectral stability problem
for every non-zero eigenvalue ![]() $\lambda _0 \in \mathbb {C} \backslash \{0\}$ must satisfy the two constraints in (1.25a,b). The spectral stability problem in the form (1.27) was also considered in Stanislavova & Stefanov (Reference Stanislavova and Stefanov2016).
$\lambda _0 \in \mathbb {C} \backslash \{0\}$ must satisfy the two constraints in (1.25a,b). The spectral stability problem in the form (1.27) was also considered in Stanislavova & Stefanov (Reference Stanislavova and Stefanov2016).
Remark 1.7 The proof of Theorem 1.2 relies on the construction of the coercive quadratic form ![]() $\langle \mathcal {L}\hat {\eta }, \hat {\eta } \rangle$ for
$\langle \mathcal {L}\hat {\eta }, \hat {\eta } \rangle$ for ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ under the three constraints
$\hat {\eta } \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ under the three constraints
The quadratic form is invariant in the time evolution of the linearized equation (1.20a,b). This yields the energetic stability of the travelling periodic wave, ensuring that the periodic wave with the profile ![]() $\eta$ is a local minimizer of the energy
$\eta$ is a local minimizer of the energy ![]() $H$ subject to fixed
$H$ subject to fixed ![]() $Q$ and
$Q$ and ![]() $M$ in
$M$ in ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. If local well posedness of the nonlinear evolution equation (1.13) can be shown in
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. If local well posedness of the nonlinear evolution equation (1.13) can be shown in ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$, then the energetic stability implies the nonlinear orbital stability of the travelling periodic wave. However, the local well posedness of (1.13) holds only in
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T})$, then the energetic stability implies the nonlinear orbital stability of the travelling periodic wave. However, the local well posedness of (1.13) holds only in ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ and the control of
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ and the control of ![]() $\| \partial _u \hat {\eta } \|_{L^{\infty }}$ for the perturbation
$\| \partial _u \hat {\eta } \|_{L^{\infty }}$ for the perturbation ![]() $\hat {\eta }$ does not follow from the conserved quantities (1.15), (1.16) and (1.18).
$\hat {\eta }$ does not follow from the conserved quantities (1.15), (1.16) and (1.18).
1.3. Discussion
The local model (1.11) shows a pattern of the existence and stability of travelling periodic waves parameterized by the wave speed ![]() $c$. There is a continuum of wave speeds for the smooth waves with profile
$c$. There is a continuum of wave speeds for the smooth waves with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ bifurcating from the linear limit in (1.21) and a continuum of wave speeds for the cusped waves with the profile
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ bifurcating from the linear limit in (1.21) and a continuum of wave speeds for the cusped waves with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^0(\mathbb {T})$ satisfying (1.22). The two continuous families are connected together at a particular value of the wave speed
$\eta \in C^0(\mathbb {T})$ satisfying (1.22). The two continuous families are connected together at a particular value of the wave speed ![]() $c = c_*$ for which the wave is peaked with the profile
$c = c_*$ for which the wave is peaked with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^0(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$. The same phenomenon is observed in the Camassa–Holm equation (Lenells Reference Lenells2005b; Geyer et al. Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022) and the Degasperis–Procesi equation (Lenells Reference Lenells2005a; Geyer & Pelinovsky Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2024).
$\eta \in C^0(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$. The same phenomenon is observed in the Camassa–Holm equation (Lenells Reference Lenells2005b; Geyer et al. Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022) and the Degasperis–Procesi equation (Lenells Reference Lenells2005a; Geyer & Pelinovsky Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2024).
It is rather remarkable that exactly the same ![]() $|u|^{2/3}$ singularity in the limiting wave profile with
$|u|^{2/3}$ singularity in the limiting wave profile with
is recovered by the local model (1.11) as predicted by the full model for any depth ![]() $h$ (Plotnikov Reference Plotnikov2002). After the conformal transformation, this singularity yields the limiting Stokes wave with the
$h$ (Plotnikov Reference Plotnikov2002). After the conformal transformation, this singularity yields the limiting Stokes wave with the ![]() $120^o$ angle in the physical coordinates. More precise details of such singular profiles are beyond the current capacities of the asymptotic (Lushnikov Reference Lushnikov2016) or numerical (Dyachenko et al. Reference Dyachenko, Lushnikov and Korotkevich2016; Lushnikov et al. Reference Lushnikov, Dyachenko and Silantyev2017) methods. The local model (1.11) gives precise conclusions that the
$120^o$ angle in the physical coordinates. More precise details of such singular profiles are beyond the current capacities of the asymptotic (Lushnikov Reference Lushnikov2016) or numerical (Dyachenko et al. Reference Dyachenko, Lushnikov and Korotkevich2016; Lushnikov et al. Reference Lushnikov, Dyachenko and Silantyev2017) methods. The local model (1.11) gives precise conclusions that the ![]() $|u|^{2/3}$ singularity is obtained in a range of wave speeds
$|u|^{2/3}$ singularity is obtained in a range of wave speeds ![]() $c$ and that the borderline wave profile
$c$ and that the borderline wave profile ![]() $\eta \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ has a peaked profile at
$\eta \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap W^{1,\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ has a peaked profile at ![]() $c = c_*$ before getting the
$c = c_*$ before getting the ![]() $|u|^{2/3}$ singularity for
$|u|^{2/3}$ singularity for ![]() $c > c_*$. This might be an artefact of the local model (1.11) since the non-local models typically predict only the
$c > c_*$. This might be an artefact of the local model (1.11) since the non-local models typically predict only the ![]() $|u|^{2/3}$ singularity in the fluid models, see Locke & Pelinovsky (Reference Locke and Pelinovsky2025).
$|u|^{2/3}$ singularity in the fluid models, see Locke & Pelinovsky (Reference Locke and Pelinovsky2025).
Stability of the travelling periodic waves with singular profiles is a complicated problem, which is out of reach in the current analytical and numerical methods in the non-local models (Dyachenko & Semenova Reference Dyachenko and Semenova2023a; Korotkevich et al. Reference Korotkevich, Lushnikov, Semenova and Dyachenko2023). The local model (1.11) is a promising candidate for showing linear instability of the peaked wave (based on a similar analysis in Geyer & Pelinovsky Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2019, Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2020; Madiyeva & Pelinovsky Reference Madiyeva and Pelinovsky2021) and for attacking linear instability of the cusped wave with the ![]() $|u|^{2/3}$ singularity.
$|u|^{2/3}$ singularity.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 contains the proof of Theorem 1.1 on the existence of smooth and peaked periodic waves. Section 3 gives the proof of Theorem 1.2 on linear stability of the smooth periodic waves. Appendix A reviews the Euler equations after the conformal transformation and discusses how the non-local model (1.1) arises. Appendix B describes the local model (1.11) in the context of other phenomenological models for dynamics of fluid surfaces.
2. Existence of smooth and peaked travelling periodic waves
We consider the single-lobe periodic solutions of the second-order equation (1.19). Recall that a single-lobe periodic solution has the even profile ![]() $\eta$ with a single maximum on
$\eta$ with a single maximum on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$ placed at
$\mathbb {T}$ placed at ![]() $u = 0$. Theorem 1.1 is proven by using the period function for the planar Hamiltonian systems used in a similar context in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022), Geyer & Pelinovsky (Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2017, Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2024) and Long & Liu (Reference Long and Liu2023).
$u = 0$. Theorem 1.1 is proven by using the period function for the planar Hamiltonian systems used in a similar context in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022), Geyer & Pelinovsky (Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2017, Reference Geyer and Pelinovsky2024) and Long & Liu (Reference Long and Liu2023).
We start with the first-order invariant of the second-order equation (1.19) given by the following lemma.
Lemma 2.1 For every solution ![]() $\eta \in C^2(a,b)$ of the second-order equation (1.19) with
$\eta \in C^2(a,b)$ of the second-order equation (1.19) with ![]() $-\infty \leq a < b \leq \infty$, the following function:
$-\infty \leq a < b \leq \infty$, the following function:
is constant for ![]() $u \in (a,b)$.
$u \in (a,b)$.
Proof. It is based on the elementary computation
 \begin{align} \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} u} E(\eta,\eta') &= (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta' \eta'' - (\eta')^3 + \eta \eta' \nonumber\\ &= \eta' [(c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta'' - (\eta')^2 + \eta] \nonumber\\ &= 0, \end{align}
\begin{align} \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} u} E(\eta,\eta') &= (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta' \eta'' - (\eta')^3 + \eta \eta' \nonumber\\ &= \eta' [(c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta'' - (\eta')^2 + \eta] \nonumber\\ &= 0, \end{align}
since ![]() $\eta \in C^2(a,b)$ satisfies (1.19).
$\eta \in C^2(a,b)$ satisfies (1.19).
The next lemma explores the phase portrait for the second-order equation (1.19) on the phase plane ![]() $(\eta,\eta ')$ obtained from the level curves of
$(\eta,\eta ')$ obtained from the level curves of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ')$ in (2.1). We obtain the existence of smooth and singular solutions in terms of the level
$E(\eta,\eta ')$ in (2.1). We obtain the existence of smooth and singular solutions in terms of the level ![]() $\mathcal {E}$ of
$\mathcal {E}$ of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ')$.
$E(\eta,\eta ')$.
Lemma 2.2 For every ![]() $c > 0$, there exists
$c > 0$, there exists ![]() $\mathcal {E}_c := {c^4}/{8}$ such that every periodic solution to (1.19) with profile
$\mathcal {E}_c := {c^4}/{8}$ such that every periodic solution to (1.19) with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$ belongs to
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$ belongs to ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with ![]() $\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$. For
$\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$. For ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}_c$, the only solution to (1.19) is the parabola
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}_c$, the only solution to (1.19) is the parabola
with arbitrary ![]() $u_0 \in \mathbb {R}$. For
$u_0 \in \mathbb {R}$. For ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with ![]() $\mathcal {E}\in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$, there exist no bounded solutions to (1.19) with profile
$\mathcal {E}\in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$, there exist no bounded solutions to (1.19) with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$.
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$.
Proof. The only equilibrium point of (1.19) is the centre ![]() $(\eta,\eta ') = (0,0)$, which corresponds to the minimum of
$(\eta,\eta ') = (0,0)$, which corresponds to the minimum of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ')$ if
$E(\eta,\eta ')$ if ![]() $c > 0$. Every periodic solution to (1.19) belongs to the period annulus, which is the largest punctured neighbourhood of the centre
$c > 0$. Every periodic solution to (1.19) belongs to the period annulus, which is the largest punctured neighbourhood of the centre ![]() $(0,0)$ consisting entirely of periodic orbits.
$(0,0)$ consisting entirely of periodic orbits.
The phase portrait from the level curves of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ is shown on figure 3. Each level curve defines the profile
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ is shown on figure 3. Each level curve defines the profile ![]() $\eta$ from integration of
$\eta$ from integration of
The vertical line corresponds to ![]() $\eta = {c^2}/{2}$ and divides the phase plane into two half-planes. For
$\eta = {c^2}/{2}$ and divides the phase plane into two half-planes. For ![]() $\eta > {c^2}/{2}$, the level curves of
$\eta > {c^2}/{2}$, the level curves of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ contain no bounded solutions. For
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ contain no bounded solutions. For ![]() $\eta < {c^2}/{2}$, bounded level curves exist for
$\eta < {c^2}/{2}$, bounded level curves exist for ![]() $\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$ with
$\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$ with ![]() $\mathcal {E}_c := {c^4}/{8}$ and contain periodic solutions with profile
$\mathcal {E}_c := {c^4}/{8}$ and contain periodic solutions with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$. For
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$. For ![]() $\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$, all solutions are given by integrating
$\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$, all solutions are given by integrating
Differentiating in ![]() $u$ gives
$u$ gives ![]() $\eta ''(u) = \frac {1}{4}$. Integrating twice and using (2.5) yields (2.3) with profile
$\eta ''(u) = \frac {1}{4}$. Integrating twice and using (2.5) yields (2.3) with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$. Finally, for
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$. Finally, for ![]() $\mathcal {E} > \mathcal {E}_c$, the level curve reaches
$\mathcal {E} > \mathcal {E}_c$, the level curve reaches ![]() $\eta = {c^2}/{2}$ with the singularity of
$\eta = {c^2}/{2}$ with the singularity of ![]() $\eta '$, which rules out the existence of bounded solutions with profile
$\eta '$, which rules out the existence of bounded solutions with profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$.
$\eta \in C^{\infty }(\mathbb {R})$.

Figure 3. Phase portrait from the level curves of ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ for
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ for ![]() $c = 1$.
$c = 1$.
The next lemma clarifies how the solutions for ![]() $\eta < {c^2}/{2}$ reach the singularity line
$\eta < {c^2}/{2}$ reach the singularity line ![]() $\eta = {c^2}/{2}$.
$\eta = {c^2}/{2}$.
Lemma 2.3 Let ![]() $\eta \in C^0(u_-,u_+)$ be a solution for the level curve
$\eta \in C^0(u_-,u_+)$ be a solution for the level curve ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ for
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ for ![]() $\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ such that
$\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ such that ![]() $\eta (u) \to \pm {c^2}/{2}$ as
$\eta (u) \to \pm {c^2}/{2}$ as ![]() $u \to u_{\pm }$. Then,
$u \to u_{\pm }$. Then, ![]() $-\infty < u_- < u_+ < \infty$ and the solution satisfies
$-\infty < u_- < u_+ < \infty$ and the solution satisfies
Proof. We consider the level curve ![]() $E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with
$E(\eta,\eta ') = \mathcal {E}$ with ![]() $\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ for
$\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ for ![]() $\eta < {c^2}/{2}$. Then, we have
$\eta < {c^2}/{2}$. Then, we have
 \begin{align} \left(\frac{{\rm d} \eta}{{\rm d} u} \right)^2 &= \frac{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}{c^2 - 2 \eta} \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2(\mathcal{E} - \mathcal{E}_c)}{c^2 - 2 \eta} + \frac{1}{2} c^2 + \frac{1}{4} (2 \eta - c^2) \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2(\mathcal{E} - \mathcal{E}_c)}{c^2 - 2 \eta} + O(1) \quad {\rm as}\ \eta \to \frac{c^2}{2}. \end{align}
\begin{align} \left(\frac{{\rm d} \eta}{{\rm d} u} \right)^2 &= \frac{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}{c^2 - 2 \eta} \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2(\mathcal{E} - \mathcal{E}_c)}{c^2 - 2 \eta} + \frac{1}{2} c^2 + \frac{1}{4} (2 \eta - c^2) \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2(\mathcal{E} - \mathcal{E}_c)}{c^2 - 2 \eta} + O(1) \quad {\rm as}\ \eta \to \frac{c^2}{2}. \end{align}This yields
Integrating in ![]() $u$ yields
$u$ yields
which results in the expansion (2.6). It remains to prove that ![]() $[u_-,u_+]$ is compact. This follows from the bounds
$[u_-,u_+]$ is compact. This follows from the bounds
 \begin{align} u_+- u_- &= 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta \nonumber\\ &\leq 2 \sqrt{c^2 +2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{{\rm d}\eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} < \infty, \end{align}
\begin{align} u_+- u_- &= 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta \nonumber\\ &\leq 2 \sqrt{c^2 +2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{{\rm d}\eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} < \infty, \end{align}since the integral in the upper bound is finite.
In order to analyse bounded periodic solutions in Lemma 2.2, we introduce the following period function associated with (2.1) and (2.4):
 \begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}
For the singular solutions in Lemma 2.3, we augment the period function for ![]() $\mathcal {E} \geq \mathcal {E}_c$ as
$\mathcal {E} \geq \mathcal {E}_c$ as
 \begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in [\mathcal{E}_c,\infty). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in [\mathcal{E}_c,\infty). \end{equation}
The next result describes properties of the period function ![]() $(0,\infty ) \ni \mathcal {E} \mapsto T(\mathcal {E},c)$ for every fixed
$(0,\infty ) \ni \mathcal {E} \mapsto T(\mathcal {E},c)$ for every fixed ![]() $c > 0$.
$c > 0$.
Lemma 2.4 For every ![]() $c > 0$, there exist
$c > 0$, there exist ![]() $\mathcal {E}_*, \mathcal {E}_{**} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ that depend on
$\mathcal {E}_*, \mathcal {E}_{**} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ that depend on ![]() $c$ such that
$c$ such that
and
with
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} T(\mathcal{E},c) \to 2 {\rm \pi}c \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E} \to 0, \\ T(\mathcal{E},c) \to 4 \sqrt{2} c \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E} \to \mathcal{E}_c, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} T(\mathcal{E},c) \to 2 {\rm \pi}c \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E} \to 0, \\ T(\mathcal{E},c) \to 4 \sqrt{2} c \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E} \to \mathcal{E}_c, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
and ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) \to \infty$ as
$T(\mathcal {E},c) \to \infty$ as ![]() $\mathcal {E}\to \infty$. In addition, we have
$\mathcal {E}\to \infty$. In addition, we have
Proof. For the smooth periodic solutions, we use the change of variables ![]() $\eta = \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}} x$ in (2.11) and obtain
$\eta = \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}} x$ in (2.11) and obtain
 \begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2 \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}}{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x},\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2 \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}}{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x},\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}
Since the weak singularity is independent of ![]() $\mathcal {E}$, we can differentiate under the integration sign and obtain
$\mathcal {E}$, we can differentiate under the integration sign and obtain
 \begin{equation} \frac{\partial}{\partial \mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\frac{2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{x\,{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}},\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \frac{\partial}{\partial \mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\frac{2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{x\,{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}},\quad \mathcal{E}\in (0,\mathcal{E}_c). \end{equation}The result is strictly negative since
 \begin{equation} \frac{|x|}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} |x|}} < \frac{x}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}, \quad x \in (0,1). \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \frac{|x|}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} |x|}} < \frac{x}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}, \quad x \in (0,1). \end{equation}
This proves (2.13) for ![]() $\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$. We also obtain from the same representation
$\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$. We also obtain from the same representation
and
Monotonicity (2.16) follows from the positive derivative of (2.11) in ![]() $c$.
$c$.
For the singular solutions, we break (2.12) into the sum of two terms and use the same change of variables only in the first term
 \begin{align} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2 \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} + 2 \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in [\mathcal{E}_c,\infty). \end{align}
\begin{align} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2 \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} + 2 \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta,\quad \mathcal{E}\in [\mathcal{E}_c,\infty). \end{align}
Since ![]() $8 \mathcal {E} > c^4$, both terms are differentiable under the integration sign and we obtain
$8 \mathcal {E} > c^4$, both terms are differentiable under the integration sign and we obtain
 \begin{align} \frac{\partial}{\partial \mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\frac{2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{x \,{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}} - 2 \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{(2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2)^3}} {\rm d} \eta, \end{align}
\begin{align} \frac{\partial}{\partial \mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\frac{2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{x \,{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}} - 2 \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{(2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2)^3}} {\rm d} \eta, \end{align}
where the first term is positive and the second term is negative. The first term is zero as ![]() $\mathcal {E} \to \mathcal {E}_c$, monotonically increasing for
$\mathcal {E} \to \mathcal {E}_c$, monotonically increasing for ![]() $\mathcal {E} \gtrsim \mathcal {E}_c$ and monotonically decreasing as
$\mathcal {E} \gtrsim \mathcal {E}_c$ and monotonically decreasing as ![]() $\mathcal {E} \to \infty$. The second term is strictly negative as
$\mathcal {E} \to \infty$. The second term is strictly negative as ![]() $\mathcal {E} \to \mathcal {E}_c$ and is monotonically increasing towards
$\mathcal {E} \to \mathcal {E}_c$ and is monotonically increasing towards ![]() $0$ for
$0$ for ![]() $\mathcal {E} > \mathcal {E}_c$. Since
$\mathcal {E} > \mathcal {E}_c$. Since
 \begin{equation} \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} \sim (8 \mathcal{E})^{1/4} \int_{-1}^0 \frac{\sqrt{|x|}{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E}\to \infty , \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \int_{-1}^{-c^2/2\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} x}}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} \sim (8 \mathcal{E})^{1/4} \int_{-1}^0 \frac{\sqrt{|x|}{{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E}\to \infty , \end{equation}and
 \begin{equation} \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta \sim (2 \mathcal{E})^{-1/2} \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E}\to \infty , \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta \sim (2 \mathcal{E})^{-1/2} \int_{-c^2/2}^{c^2/2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta \quad {\rm as}\ \mathcal{E}\to \infty , \end{equation}
the first term in the decomposition (2.23) is larger than the second term at infinity and we have ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = {O}(\mathcal {E}^{1/4})$ as
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = {O}(\mathcal {E}^{1/4})$ as ![]() $\mathcal {E} \to \infty$ so that
$\mathcal {E} \to \infty$ so that
At the same time, the first term in the decomposition (2.23) is zero at ![]() $\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$, hence there exist
$\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$, hence there exist ![]() $\mathcal {E}_*,\mathcal {E}_{**} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ such that (2.13) and (2.14) hold. Monotonicity (2.16) follows from the positive derivative of (2.12) in
$\mathcal {E}_*,\mathcal {E}_{**} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ such that (2.13) and (2.14) hold. Monotonicity (2.16) follows from the positive derivative of (2.12) in ![]() $c$.
$c$.
We are now ready to prove Theorem 1.1.
Proof of Theorem 1.1 We consider the family of solutions of Lemmas 2.2 and 2.3 for ![]() $\mathcal {E}\in (0,\infty )$ and
$\mathcal {E}\in (0,\infty )$ and ![]() $\eta < {c^2}/{2}$. For every
$\eta < {c^2}/{2}$. For every ![]() $c > 0$, we select the intersection of the period function
$c > 0$, we select the intersection of the period function ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c)$ of Lemma 2.4 with the
$T(\mathcal {E},c)$ of Lemma 2.4 with the ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$ period on
$2{\rm \pi}$ period on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$. It follows from (2.16) that the period function is monotonically increasing in
$\mathbb {T}$. It follows from (2.16) that the period function is monotonically increasing in ![]() $c$ for every
$c$ for every ![]() $\mathcal {E} \in (0,\infty )$.
$\mathcal {E} \in (0,\infty )$.
For the smooth periodic solutions with the period function (2.11), there exists only one root ![]() $\mathcal {E} \in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$ of
$\mathcal {E} \in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)$ of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for every
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for every ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ with
$c \in (1,c_*)$ with ![]() $c_* = {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$ due to monotonicity (2.13) and the limiting values
$c_* = {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$ due to monotonicity (2.13) and the limiting values ![]() $T(0,c) = 2 {\rm \pi}c$ and
$T(0,c) = 2 {\rm \pi}c$ and ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2} c$. This gives the first assertion of the theorem with the limit (1.21) since the smooth periodic solution shrinks to the centre point
$T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2} c$. This gives the first assertion of the theorem with the limit (1.21) since the smooth periodic solution shrinks to the centre point ![]() $(0,0)$ on the
$(0,0)$ on the ![]() $(\eta,\eta ')$ plane as
$(\eta,\eta ')$ plane as ![]() $\mathcal {E}\to 0$. At
$\mathcal {E}\to 0$. At ![]() $c = c_*$, we have
$c = c_*$, we have ![]() $\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_{c_*}$ for the root of
$\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_{c_*}$ for the root of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The unique single-lobe solution (1.23) follows from the unique solution (2.3) at
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The unique single-lobe solution (1.23) follows from the unique solution (2.3) at ![]() $\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$ from Lemma 2.2 by the translation
$\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}_c$ from Lemma 2.2 by the translation ![]() $u_0 = {\rm \pi}$ for
$u_0 = {\rm \pi}$ for ![]() $u \in [0,{\rm \pi} ]$ and an even reflection on
$u \in [0,{\rm \pi} ]$ and an even reflection on ![]() $[-{\rm \pi},0]$.
$[-{\rm \pi},0]$.
For the singular solutions with the period function (2.12), we have a root ![]() $\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ of
$\mathcal {E} \in (\mathcal {E}_c,\infty )$ of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for every
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for every ![]() $c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$ due to monotonicity (2.13). The value
$c \in (c_*,c_{\infty })$ due to monotonicity (2.13). The value ![]() $c_{\infty }$ is obtained from the intersection of
$c_{\infty }$ is obtained from the intersection of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}_*,c)$ with
$T(\mathcal {E}_*,c)$ with ![]() $2 {\rm \pi}$. The asymptotic expansion (1.22) of the singular single-lobe solutions follows from the expansion (2.6) with the translation
$2 {\rm \pi}$. The asymptotic expansion (1.22) of the singular single-lobe solutions follows from the expansion (2.6) with the translation ![]() $u_- = 0$ of the solution in Lemma 2.3 for
$u_- = 0$ of the solution in Lemma 2.3 for ![]() $u \in [0,{\rm \pi} ]$ with
$u \in [0,{\rm \pi} ]$ with ![]() $\eta ({\rm \pi} ) = -\sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}}$ and
$\eta ({\rm \pi} ) = -\sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}}$ and ![]() $\eta '({\rm \pi} ) = 0$ and an even reflection on
$\eta '({\rm \pi} ) = 0$ and an even reflection on ![]() $[-{\rm \pi},0]$.
$[-{\rm \pi},0]$.
Figure 4 illustrates the result of Lemma 2.4 and the proof of Theorem 1.1. The period functions (2.11) and (2.12) can be computed in terms of complete elliptic integrals by using 3.141 (integrals 2 and 9) in Gradshteyn & Ryzhik (Reference Gradshteyn and Ryzhik2007)
 \begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 4 \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} E\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right),\quad \mathcal{E} \in (0,\mathcal{E}_c), \end{equation}
\begin{equation} T(\mathcal{E},c) = 4 \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} E\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right),\quad \mathcal{E} \in (0,\mathcal{E}_c), \end{equation}and
 \begin{align} T(\mathcal{E},c) &= 4 (2\mathcal{E})^{1/4} \left[2 E\left(\sqrt{\frac{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}} \right) \right. \nonumber\\ &\quad \left.+ \left(\frac{c^2}{2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} - 1 \right) K \left(\sqrt{\frac{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right)\right],\quad \mathcal{E} \in (\mathcal{E}_c,\infty), \end{align}
\begin{align} T(\mathcal{E},c) &= 4 (2\mathcal{E})^{1/4} \left[2 E\left(\sqrt{\frac{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}} \right) \right. \nonumber\\ &\quad \left.+ \left(\frac{c^2}{2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} - 1 \right) K \left(\sqrt{\frac{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right)\right],\quad \mathcal{E} \in (\mathcal{E}_c,\infty), \end{align}
where ![]() $K(k)$ and
$K(k)$ and ![]() $E(k)$ are complete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The two definitions agree at
$E(k)$ are complete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The two definitions agree at ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2} c$, where
$T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2} c$, where ![]() $\mathcal {E}_c = {c^4}/{8}$ shown by the black dot in figure 4. We can also see from figure 4 that the monotonicity results (2.13), (2.14) and (2.16) hold true with
$\mathcal {E}_c = {c^4}/{8}$ shown by the black dot in figure 4. We can also see from figure 4 that the monotonicity results (2.13), (2.14) and (2.16) hold true with ![]() $\mathcal {E}_* = \mathcal {E}_{**}$. The periodic solutions of Theorem 1.1 on
$\mathcal {E}_* = \mathcal {E}_{**}$. The periodic solutions of Theorem 1.1 on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$ are obtained by the intersection of the plot of the period function with the level
$\mathbb {T}$ are obtained by the intersection of the plot of the period function with the level ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$.
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$.

Figure 4. Period function ![]() $T$ vs
$T$ vs ![]() $\mathcal {E}$ for
$\mathcal {E}$ for ![]() $c = 1.05$ (solid blue) and
$c = 1.05$ (solid blue) and ![]() $c = 1.1$ (dashed blue). Black dots show the values
$c = 1.1$ (dashed blue). Black dots show the values ![]() $T(0,c) = 2{\rm \pi} c$ and
$T(0,c) = 2{\rm \pi} c$ and ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2}c$. The red dashed line gives the level
$T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 4 \sqrt {2}c$. The red dashed line gives the level ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for periodic solutions on
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ for periodic solutions on ![]() $\mathbb {T}$.
$\mathbb {T}$.
3. Stability of smooth travelling periodic waves
We consider the unique single-lobe solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ in Theorem 1.1 which exists in the second-order equation (1.19) for
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ in Theorem 1.1 which exists in the second-order equation (1.19) for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ with
$c \in (1,c_*)$ with ![]() $c_* = {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$. Theorem 1.2 is proven by showing that the periodic solution is a constrained minimizer of the quadratic form
$c_* = {\rm \pi}/(2\sqrt{2})$. Theorem 1.2 is proven by showing that the periodic solution is a constrained minimizer of the quadratic form ![]() $\langle \mathcal {L}\hat {\eta }, \hat {\eta } \rangle$ associated with the linear operator
$\langle \mathcal {L}\hat {\eta }, \hat {\eta } \rangle$ associated with the linear operator
in the function space ![]() $H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$, where
$H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$, where
The minimizer is only degenerate due to the translational symmetry which results in the one-dimensional kernel ![]() ${\rm Ker}(\mathcal {L}) = {\rm span}(\eta ')$ with
${\rm Ker}(\mathcal {L}) = {\rm span}(\eta ')$ with ![]() $\eta ' \in \mathcal {X}_c$.
$\eta ' \in \mathcal {X}_c$.
We start with the count of the negative eigenvalues of ![]() $\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ in the following lemma.
$\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ in the following lemma.
Lemma 3.1 Let ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ be the profile of the single-lobe solution in Theorem 1.1 for
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ be the profile of the single-lobe solution in Theorem 1.1 for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ and
$c \in (1,c_*)$ and ![]() $\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ be the linear operator given by (3.1). Then,
$\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ be the linear operator given by (3.1). Then, ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ has two simple negative eigenvalues and a simple zero eigenvalue, with the rest of its spectrum bounded away from zero.
$\mathcal {L}$ has two simple negative eigenvalues and a simple zero eigenvalue, with the rest of its spectrum bounded away from zero.
Proof. Since ![]() $\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is a self-adjoint Sturm–Liouville operator with
$\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ is a self-adjoint Sturm–Liouville operator with ![]() $\eta '' \in L^{\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ and
$\eta '' \in L^{\infty }(\mathbb {T})$ and ![]() $c^2 - 2 \eta (u) > 0$ for every
$c^2 - 2 \eta (u) > 0$ for every ![]() $u \in \mathbb {T}$, its spectrum consists of isolated eigenvalues located on the real line.
$u \in \mathbb {T}$, its spectrum consists of isolated eigenvalues located on the real line.
For fixed ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$, differentiating (1.19) in
$c \in (1,c_*)$, differentiating (1.19) in ![]() $u$ yields
$u$ yields ![]() $\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$ with
$\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$ with ![]() $\eta ' \in H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Hence,
$\eta ' \in H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Hence, ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ admits a zero eigenvalue with the spatially odd eigenfunction
$\mathcal {L}$ admits a zero eigenvalue with the spatially odd eigenfunction ![]() $\eta '$. To consider the second linearly independent solution of
$\eta '$. To consider the second linearly independent solution of ![]() $\mathcal {L} \hat {\eta } = 0$, we define the family
$\mathcal {L} \hat {\eta } = 0$, we define the family ![]() $\{ \eta (u;\mathcal {E})\}_{\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)}$ of spatially even, smooth periodic solutions of the second-order equation (1.19) with
$\{ \eta (u;\mathcal {E})\}_{\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)}$ of spatially even, smooth periodic solutions of the second-order equation (1.19) with
and
where ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c)$ is the period function (2.11) satisfying (2.13). Let
$T(\mathcal {E},c)$ is the period function (2.11) satisfying (2.13). Let ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c)$ be the root of the period function
$\mathcal {E}(c)$ be the root of the period function ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ in the proof of Theorem 1.1 such that
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ in the proof of Theorem 1.1 such that ![]() $\eta (u) = \eta (u;\mathcal {E}(c)) \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Differentiating (1.19) in
$\eta (u) = \eta (u;\mathcal {E}(c)) \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Differentiating (1.19) in ![]() $\mathcal {E}$ along the family
$\mathcal {E}$ along the family ![]() $\{ \eta (u;\mathcal {E})\}_{\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)}$ and setting
$\{ \eta (u;\mathcal {E})\}_{\mathcal {E}\in (0,\mathcal {E}_c)}$ and setting ![]() $\mathcal {E}= \mathcal {E}(c)$ yields the second linearly independent solution of
$\mathcal {E}= \mathcal {E}(c)$ yields the second linearly independent solution of ![]() $\mathcal {L} \hat {\eta } = 0$. The solution is given by the spatially even function
$\mathcal {L} \hat {\eta } = 0$. The solution is given by the spatially even function ![]() $\partial _{\mathcal {E}} \eta ({\cdot };\mathcal {E}(c))$ which satisfies
$\partial _{\mathcal {E}} \eta ({\cdot };\mathcal {E}(c))$ which satisfies
and
where we have used (1.19) at ![]() $u = T(\mathcal {E},c)$ which implies
$u = T(\mathcal {E},c)$ which implies
We thus have ![]() $\partial _{\mathcal {E}} \eta ({\cdot };\mathcal {E}(c)) \in H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ if and only if
$\partial _{\mathcal {E}} \eta ({\cdot };\mathcal {E}(c)) \in H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ if and only if ![]() $\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 0$, which is impossible due to monotonicity (2.13). Hence,
$\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 0$, which is impossible due to monotonicity (2.13). Hence, ![]() $0$ is a simple eigenvalue of
$0$ is a simple eigenvalue of ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ bounded away from the rest of its spectrum in
$\mathcal {L}$ bounded away from the rest of its spectrum in ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$.
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$.
To prove that there exist two negative eigenvalues of ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ below the zero eigenvalue, we use Proposition 1 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022) and construct the following two normalized solutions:
$\mathcal {L}$ below the zero eigenvalue, we use Proposition 1 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022) and construct the following two normalized solutions:
where ![]() $\eta _2(u+2{\rm \pi} ) = \eta _2(u)$ and
$\eta _2(u+2{\rm \pi} ) = \eta _2(u)$ and ![]() $\eta _1(u+2{\rm \pi} ) = \eta _1(u) + \theta \eta _2(u)$ with
$\eta _1(u+2{\rm \pi} ) = \eta _1(u) + \theta \eta _2(u)$ with
 \begin{equation} \theta := \partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E}(c),c) \frac{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}(c)}}{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}(c)}} < 0, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \theta := \partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E}(c),c) \frac{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}(c)}}{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}(c)}} < 0, \end{equation}
due to monotonicity (2.13). By Proposition 1 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022), ![]() $0$ is the third eigenvalue of
$0$ is the third eigenvalue of ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ with two simple negative eigenvalues below
$\mathcal {L}$ with two simple negative eigenvalues below ![]() $0$.
$0$.
Remark 3.1 One can prove the assertion of Lemma 3.1 by using small-amplitude expansions. The periodic solution with the profile ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ is expanded near the trivial solution, see (1.21), as
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$ is expanded near the trivial solution, see (1.21), as
where ![]() $a > 0$ is a small parameter. Then,
$a > 0$ is a small parameter. Then, ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ along the solution family has one negative eigenvalue
$\mathcal {L}$ along the solution family has one negative eigenvalue ![]() $-1 + {O}(a^2)$ and a small negative eigenvalue
$-1 + {O}(a^2)$ and a small negative eigenvalue ![]() $-a^2 + {O}(a^4)$ with
$-a^2 + {O}(a^4)$ with ![]() $0$ being the third eigenvalue. Since
$0$ being the third eigenvalue. Since ![]() ${\rm Ker}(\mathcal {L}) = {\rm span}(\eta ')$ along the family of smooth periodic solutions for
${\rm Ker}(\mathcal {L}) = {\rm span}(\eta ')$ along the family of smooth periodic solutions for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$, the inertia index of
$c \in (1,c_*)$, the inertia index of ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ remains the same for every
$\mathcal {L}$ remains the same for every ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$.
$c \in (1,c_*)$.
The next lemma specifies the criterion for the constrained linear operator ![]() $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ to be positive, where
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ to be positive, where ![]() $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c} = \mathcal {L} |_{\{ 1, \eta ''\}^{\perp }}$ is defined by the two constraints in (3.2).
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c} = \mathcal {L} |_{\{ 1, \eta ''\}^{\perp }}$ is defined by the two constraints in (3.2).
Lemma 3.2 Let ![]() $\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ be given by (3.1) as in Lemma 3.1 and
$\mathcal {L} : H^2_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \subset L^2(\mathbb {T}) \to L^2(\mathbb {T})$ be given by (3.1) as in Lemma 3.1 and ![]() $\mathcal {X}_c$ be the constrained subspace of
$\mathcal {X}_c$ be the constrained subspace of ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$ given by (3.2). Then,
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$ given by (3.2). Then, ![]() $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ has a simple zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues, with the rest of its spectrum being bounded away from zero, if and only if the mapping
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ has a simple zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues, with the rest of its spectrum being bounded away from zero, if and only if the mapping
is monotonically decreasing for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$.
$c \in (1,c_*)$.
Proof. By Proposition 2 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022), we construct the ![]() $2$-by-
$2$-by-![]() $2$ matrix related to the two constraints in
$2$ matrix related to the two constraints in ![]() $\mathcal {X}_c$
$\mathcal {X}_c$
The inverse operator ![]() $\mathcal {L}^{-1}$ on
$\mathcal {L}^{-1}$ on ![]() ${\rm span}(1,\eta '')$ is well defined since
${\rm span}(1,\eta '')$ is well defined since
Differentiating (1.19) in ![]() $c$ yields
$c$ yields
where ![]() $\partial _c \eta$ is defined along the family of
$\partial _c \eta$ is defined along the family of ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic solutions ![]() $\{ \eta \}_{c \in (1,c_*)}$. The family is smooth in
$\{ \eta \}_{c \in (1,c_*)}$. The family is smooth in ![]() $c$ since
$c$ since ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c)$ is
$T(\mathcal {E},c)$ is ![]() $C^1$ on
$C^1$ on ![]() $(0,\mathcal {E}_c) \times (0,c_*)$ and
$(0,\mathcal {E}_c) \times (0,c_*)$ and ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c)$ is
$\mathcal {E}(c)$ is ![]() $C^1$ on
$C^1$ on ![]() $(0,c_*)$ due to the implicit function theorem for
$(0,c_*)$ due to the implicit function theorem for ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ with
$T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ with ![]() $\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$. In addition, we have
$\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$. In addition, we have ![]() $\mathcal {L} 1 = 2 \eta '' - 1$ so that
$\mathcal {L} 1 = 2 \eta '' - 1$ so that
By using (3.14) and (3.15), we compute
Since ![]() $A$ is symmetric, we have
$A$ is symmetric, we have ![]() $\langle \partial _c \eta, 1 \rangle = 2 \langle \partial _c \eta, \eta '' \rangle$. Furthermore,
$\langle \partial _c \eta, 1 \rangle = 2 \langle \partial _c \eta, \eta '' \rangle$. Furthermore,
where ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c)$ is given by (3.11). Since
$\mathcal {M}(c)$ is given by (3.11). Since ![]() $c > 0$, we have the following trichotomy from Proposition 2 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022):
$c > 0$, we have the following trichotomy from Proposition 2 in Geyer et al. (Reference Geyer, Martins, Natali and Pelinovsky2022):
(i) If
 $\mathcal {M}'(c) > 0$, then
$\mathcal {M}'(c) > 0$, then  $\det (A) < 0$, hence
$\det (A) < 0$, hence  $A$ has one negative and one positive eigenvalue so that
$A$ has one negative and one positive eigenvalue so that  $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits one simple negative and a simple zero eigenvalue.
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits one simple negative and a simple zero eigenvalue.(ii) If
 $\mathcal {M}'(c) = 0$, then
$\mathcal {M}'(c) = 0$, then  $\det (A) = 0$ but
$\det (A) = 0$ but  ${\rm tr}(A) < 0$, hence
${\rm tr}(A) < 0$, hence  $A$ has one negative and one zero eigenvalue so that
$A$ has one negative and one zero eigenvalue so that  $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits a double zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues.
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits a double zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues.(iii) If
 $\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$, then
$\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$, then  $\det (A) > 0$, hence
$\det (A) > 0$, hence  $A$ has two negative eigenvalues so that
$A$ has two negative eigenvalues so that  $\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits a simple zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues.
$\mathcal {L}|_{\mathcal {X}_c}$ admits a simple zero eigenvalue and no negative eigenvalues.
The last case yields the assertion of the lemma.
Remark 3.2 Due to constraint (1.12), we have
so that the criterion in Lemma 3.2 is equivalent to the mapping of
being monotonically increasing for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$.
$c \in (1,c_*)$.
Since ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c) \to 0$ as
$\mathcal {M}(c) \to 0$ as ![]() $c \to 1$ by (1.21) and
$c \to 1$ by (1.21) and ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c) < 0$ by (3.18), it is clear that
$\mathcal {M}(c) < 0$ by (3.18), it is clear that ![]() $\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$ for
$\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$ for ![]() $c \gtrsim 1$. The next lemma asserts that
$c \gtrsim 1$. The next lemma asserts that ![]() $\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$ for every
$\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$ for every ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$.
$c \in (1,c_*)$.
Lemma 3.3 The mapping (3.11) is monotonically decreasing for every ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$.
$c \in (1,c_*)$.
Proof. Differentiating ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ in
$T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ in ![]() $c$ yields
$c$ yields
where
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \partial_c T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2c \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \\ \partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \partial_c T(\mathcal{E},c) = 2c \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \\ \partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E},c) =-\mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
and we have used (2.18) with the substitution ![]() $\eta = \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}}x$. By using the same substitution, we define
$\eta = \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}}x$. By using the same substitution, we define ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c) \equiv \mathcal {M}(\mathcal {E}(c),c)$ with
$\mathcal {M}(c) \equiv \mathcal {M}(\mathcal {E}(c),c)$ with
 \begin{equation} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} = 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{x \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}} x} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) := 2 \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} = 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}} \int_{-1}^{1} \frac{x \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}} x} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x}}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, \end{equation}from which we obtain
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \partial_c \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) = 2c \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \\ \partial_{\mathcal{E}} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) = \mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} } - \mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta^2 {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \partial_c \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) = 2c \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}, \\ \partial_{\mathcal{E}} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) = \mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} } - \mathcal{E}^{-1} \int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta^2 {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
Since ![]() $\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$, we obtain
$\partial _{\mathcal {E}} T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$, we obtain
 \begin{align} \mathcal{M}'(c) &= \partial_c \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E}(c),c) + \mathcal{E}'(c) \partial_{\mathcal{E}} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E}(c),c) \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2c}{\mathcal{E}(c) |\partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E}(c),c)|} \varDelta(\mathcal{E}(c),c), \end{align}
\begin{align} \mathcal{M}'(c) &= \partial_c \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E}(c),c) + \mathcal{E}'(c) \partial_{\mathcal{E}} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E}(c),c) \nonumber\\ &= \frac{2c}{\mathcal{E}(c) |\partial_{\mathcal{E}} T(\mathcal{E}(c),c)|} \varDelta(\mathcal{E}(c),c), \end{align}where
 \begin{align} \varDelta(\mathcal{E},c) &:= \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} \right)^2 \nonumber\\ &\quad + \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta (c^2 - 3 \eta) \,{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right). \end{align}
\begin{align} \varDelta(\mathcal{E},c) &:= \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} \right)^2 \nonumber\\ &\quad + \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta (c^2 - 3 \eta) \,{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right). \end{align}
We show that ![]() $\varDelta (\mathcal {E},c) < 0$, which implies that
$\varDelta (\mathcal {E},c) < 0$, which implies that ![]() $\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$. Indeed, since
$\mathcal {M}'(c) < 0$. Indeed, since
 \begin{equation} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} < \frac{|\eta| \sqrt{c^2 + 2 |\eta|}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}},\quad \eta \in (0,\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}), \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} < \frac{|\eta| \sqrt{c^2 + 2 |\eta|}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}},\quad \eta \in (0,\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}), \end{equation}we have
 \begin{equation} \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} \right) \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} \right) < 0. \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} \right) \left(\int_{-\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}} \frac{\eta \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta} {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2}} \right) < 0. \end{equation}
The remaining part of ![]() $\varDelta (\mathcal {E},c)$ is also negative since
$\varDelta (\mathcal {E},c)$ is also negative since
 \begin{align} & \left(\int \frac{\eta \,{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right)^2 - \left(\int \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \left(\int\frac{\eta^2 {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \nonumber\\ &\quad = \int\int \frac{\eta_1 \eta_2 - \eta_2^2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_1^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_1} \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_2^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_2}} {\rm d} \eta_1 \,{\rm d} \eta_2 \nonumber\\ &\quad =-\frac{1}{2} \int\int \frac{(\eta_1-\eta_2)^2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_1^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_1} \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_2^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_2}} {\rm d} \eta_1 \,{\rm d} \eta_2 < 0, \end{align}
\begin{align} & \left(\int \frac{\eta \,{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right)^2 - \left(\int \frac{{\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \left(\int\frac{\eta^2 {\rm d} \eta}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}\right) \nonumber\\ &\quad = \int\int \frac{\eta_1 \eta_2 - \eta_2^2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_1^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_1} \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_2^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_2}} {\rm d} \eta_1 \,{\rm d} \eta_2 \nonumber\\ &\quad =-\frac{1}{2} \int\int \frac{(\eta_1-\eta_2)^2}{\sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_1^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_1} \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E} - \eta_2^2} \sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta_2}} {\rm d} \eta_1 \,{\rm d} \eta_2 < 0, \end{align}
where the integrations are defined on ![]() $[-\sqrt {2\mathcal {E}},\sqrt {2\mathcal {E}}]$. Hence,
$[-\sqrt {2\mathcal {E}},\sqrt {2\mathcal {E}}]$. Hence, ![]() $\varDelta (\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$ and the assertion of the lemma has been proven.
$\varDelta (\mathcal {E}(c),c) < 0$ and the assertion of the lemma has been proven.
We are now ready to prove Theorem 1.2.
Proof of Theorem 1.2 First, we prove that the two constraints (1.25a,b) are preserved in the time evolution of the linearized equation (1.20a,b). Since ![]() $\varPi _0 \partial _u^{-1} \varPi _0$ is defined on zero-mean functions with the zero-mean constraint, taking the mean value of (1.20a,b) yields
$\varPi _0 \partial _u^{-1} \varPi _0$ is defined on zero-mean functions with the zero-mean constraint, taking the mean value of (1.20a,b) yields
Multiplying (1.20a,b) by ![]() $\eta ''$ and integrating by parts, we obtain for any solution
$\eta ''$ and integrating by parts, we obtain for any solution ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$
$\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$
 \begin{align} 2c \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} t} \langle \eta'', \hat{\eta} \rangle &= \langle (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta'', \partial_u \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= \langle (\eta')^2 - \eta, \partial_u \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= \langle \eta' - 2 \eta' \eta'', \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= 0, \end{align}
\begin{align} 2c \frac{{\rm d}}{{\rm d} t} \langle \eta'', \hat{\eta} \rangle &= \langle (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta'', \partial_u \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= \langle (\eta')^2 - \eta, \partial_u \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= \langle \eta' - 2 \eta' \eta'', \hat{\eta} \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta', \hat{\eta} \rangle \nonumber\\ &= 0, \end{align}
where (1.19) has been used with ![]() $\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Hence, the two constraints (1.25a,b) are preserved in time and the solution
$\eta \in C^{\infty }_{per}(\mathbb {T})$. Hence, the two constraints (1.25a,b) are preserved in time and the solution ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b) with
$\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b) with ![]() $\hat {\eta }({\cdot },0) = \hat {\eta }_0$ and
$\hat {\eta }({\cdot },0) = \hat {\eta }_0$ and ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0 \in \mathcal {X}_c$ satisfies
$\hat {\eta }_0 \in \mathcal {X}_c$ satisfies ![]() $\hat {\eta }({\cdot },t) \in \mathcal {X}_c$ for every
$\hat {\eta }({\cdot },t) \in \mathcal {X}_c$ for every ![]() $t \in \mathbb{R}$. Thus, we have
$t \in \mathbb{R}$. Thus, we have
If we further decompose
then ![]() $w({\cdot },t) \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$ for
$w({\cdot },t) \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$ for ![]() $t \in \mathbb {R}$ satisfies the additional constraint
$t \in \mathbb {R}$ satisfies the additional constraint
Next, the existence and uniqueness of solutions ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b) such that
$\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b) such that ![]() $\hat {\eta }({\cdot },0) = \hat {\eta }_0$ follow by the energy method (Renardy & Rogers Reference Renardy and Rogers2004). The energy quadratic form
$\hat {\eta }({\cdot },0) = \hat {\eta }_0$ follow by the energy method (Renardy & Rogers Reference Renardy and Rogers2004). The energy quadratic form ![]() $\langle \mathcal {L} \hat {\eta },\hat {\eta } \rangle$ is bounded and conserved for the solution
$\langle \mathcal {L} \hat {\eta },\hat {\eta } \rangle$ is bounded and conserved for the solution ![]() $\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b). Since
$\hat {\eta } \in C^0(\mathbb {R},H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}))$ of the linearized equation (1.20a,b). Since ![]() $\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$, we get
$\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$, we get
for some fixed ![]() $\beta > 0$. By Lemmas 3.2 and 3.3,
$\beta > 0$. By Lemmas 3.2 and 3.3, ![]() $\langle \mathcal {L} w({\cdot },t), w({\cdot },t) \rangle$ is coercive for
$\langle \mathcal {L} w({\cdot },t), w({\cdot },t) \rangle$ is coercive for ![]() $w({\cdot },t) \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$ and is non-degenerate if
$w({\cdot },t) \in H^1_{per}(\mathbb {T}) \cap \mathcal {X}_c$ and is non-degenerate if ![]() $w({\cdot },t)$ is orthogonal to
$w({\cdot },t)$ is orthogonal to ![]() $\eta '$. Hence, we get the lower bound with some fixed
$\eta '$. Hence, we get the lower bound with some fixed ![]() $\alpha > 0$
$\alpha > 0$
which implies the first estimate (1.26a). In addition, we get from (1.20a,b) due to ![]() $\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$
$\mathcal {L} \eta ' = 0$
which allows us to control the unique ![]() $a \in C^1(\mathbb {R},\mathbb {R})$ from the bound
$a \in C^1(\mathbb {R},\mathbb {R})$ from the bound
 \begin{align} 2c a'(t) \| \eta' \|^2_{L^2} &= \langle (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta', \partial_u w({\cdot},t) \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta, w({\cdot},t) \rangle \nonumber\\ &\leq \gamma \| w({\cdot},t) \|_{H^1_{per}}, \end{align}
\begin{align} 2c a'(t) \| \eta' \|^2_{L^2} &= \langle (c^2 - 2 \eta) \eta', \partial_u w({\cdot},t) \rangle - \langle (1-2\eta'') \eta, w({\cdot},t) \rangle \nonumber\\ &\leq \gamma \| w({\cdot},t) \|_{H^1_{per}}, \end{align}
for some fixed ![]() $\gamma > 0$, which yields the second estimate (1.26b).
$\gamma > 0$, which yields the second estimate (1.26b).
Figure 5 displays the dependence of ![]() $\mathcal {E}$ and
$\mathcal {E}$ and ![]() $\mathcal {M}$ on
$\mathcal {M}$ on ![]() $c$ for
$c$ for ![]() $c \in (1,c_*)$ computed along the family of solutions of
$c \in (1,c_*)$ computed along the family of solutions of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The mass integral can be computed in terms of complete elliptic integrals by using 3.141 (integral 20) in Gradshteyn & Ryzhik (Reference Gradshteyn and Ryzhik2007)
$T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The mass integral can be computed in terms of complete elliptic integrals by using 3.141 (integral 20) in Gradshteyn & Ryzhik (Reference Gradshteyn and Ryzhik2007)
 \begin{align} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) &=-2 \int_{-\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}}{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} {\rm d} \eta \nonumber\\ &=-4 \mathcal{E} \int_{-1}^1 \frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}} x}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} \nonumber\\ &=- \frac{2}{3} \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} \left[c^2 E\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right) \right. \nonumber\\ &\quad \left.-\,(c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}) K\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right)\right], \end{align}
\begin{align} \mathcal{M}(\mathcal{E},c) &=-2 \int_{-\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}^{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} \frac{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E} - \eta^2}}{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}} {\rm d} \eta \nonumber\\ &=-4 \mathcal{E} \int_{-1}^1 \frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}} x}} {{\rm d}\kern0.06em x} \nonumber\\ &=- \frac{2}{3} \sqrt{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}} \left[c^2 E\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right) \right. \nonumber\\ &\quad \left.-\,(c^2 - 2 \sqrt{2 \mathcal{E}}) K\left(\sqrt{\frac{4 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}{c^2 + 2 \sqrt{2\mathcal{E}}}}\right)\right], \end{align}
where ![]() $K(k)$ and
$K(k)$ and ![]() $E(k)$ are complete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The values of
$E(k)$ are complete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The values of ![]() $\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}(c)$ are computed numerically from
$\mathcal {E} = \mathcal {E}(c)$ are computed numerically from ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ by a root-finding algorithm. Figure 5 illustrates the monotonicity result of Lemma 3.3. Since
$T(\mathcal {E}_c,c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ by a root-finding algorithm. Figure 5 illustrates the monotonicity result of Lemma 3.3. Since ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c) \to 0$ as
$\mathcal {E}(c) \to 0$ as ![]() $c \to 1$ follows from (1.21), we have
$c \to 1$ follows from (1.21), we have ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c) \to 0$ as
$\mathcal {M}(c) \to 0$ as ![]() $c \to 1$. On the other hand,
$c \to 1$. On the other hand, ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c_*) \to {c_*^4}/{8} = {{\rm \pi} ^4}/{512}$ as
$\mathcal {E}(c_*) \to {c_*^4}/{8} = {{\rm \pi} ^4}/{512}$ as ![]() $c \to c_*$ follows by Lemma 2.4 and we compute from (1.23) that
$c \to c_*$ follows by Lemma 2.4 and we compute from (1.23) that
which agrees well with the numerical data in figure 5.

Figure 5. Dependence of ![]() $\mathcal {E}$ (a) and
$\mathcal {E}$ (a) and ![]() $\mathcal {M}$ (b) on
$\mathcal {M}$ (b) on ![]() $c$ along the family of solutions of
$c$ along the family of solutions of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The black dots show the values
$T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$. The black dots show the values ![]() $\mathcal {E}(1) = 0$,
$\mathcal {E}(1) = 0$, ![]() $\mathcal {M}(1) = 0$ and
$\mathcal {M}(1) = 0$ and ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c_*) = {{\rm \pi} ^4}/{512}$,
$\mathcal {E}(c_*) = {{\rm \pi} ^4}/{512}$, ![]() $\mathcal {M}(c_*) = -({{\rm \pi} ^3}/{24})$.
$\mathcal {M}(c_*) = -({{\rm \pi} ^3}/{24})$.
Numerical methods. The numerical data in figure 2 are an extended version of figure 5(a), where all roots of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ have been computed numerically from a bisection method, see figure 4. The numerical data in figure 1 were obtained from finding roots of the implicit function
$T(\mathcal {E},c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ have been computed numerically from a bisection method, see figure 4. The numerical data in figure 1 were obtained from finding roots of the implicit function
 \begin{equation} |u| = \int_{\eta}^{\eta_{max}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}(c)-\eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} |u| = \int_{\eta}^{\eta_{max}} \frac{\sqrt{c^2 - 2 \eta}}{\sqrt{2\mathcal{E}(c)-\eta^2}} {\rm d} \eta, \end{equation}
where ![]() $\eta _{max} := \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}(c)}$ for smooth profiles (panel a) and
$\eta _{max} := \sqrt {2 \mathcal {E}(c)}$ for smooth profiles (panel a) and ![]() $\eta _{max} := {c^2}/{2}$ for singular profiles (panel b) and
$\eta _{max} := {c^2}/{2}$ for singular profiles (panel b) and ![]() $\mathcal {E}(c)$ is a root of
$\mathcal {E}(c)$ is a root of ![]() $T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ obtained on the lower part of the bifurcation diagram in figure 2.
$T(\mathcal {E}(c),c) = 2{\rm \pi}$ obtained on the lower part of the bifurcation diagram in figure 2.
Supplementary material
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the authors.
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of the undergraduate thesis of S. Locke at McMaster University (2023–2024). The authors thank S. Dyachenko, P. Lushnikov, J. Weber and X. Zhao for many discussions related to the content of this work. Figure 1 was prepared by S. Wang as a part of an undergraduate summer project (2024).
Funding
D.E.P. acknowledges the funding of this study provided by the grant no. FSWE-2023-0004 through the State task program in the sphere of scientific activity of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and grant no. NSH-70.2022.1.5 for the State support of leading Scientific Schools of the Russian Federation.
Declaration of interests
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Euler equations after a conformal transformation
Let ![]() $y = \eta (x,t)$ be the profile for the free surface of an incompressible and irrotational fluid in the
$y = \eta (x,t)$ be the profile for the free surface of an incompressible and irrotational fluid in the ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic domain and assume a flat bottom at
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic domain and assume a flat bottom at ![]() $y = -h_0$, where the vertical velocity vanishes. For a proper definition of the fluid depth
$y = -h_0$, where the vertical velocity vanishes. For a proper definition of the fluid depth ![]() $h_0$, we add the zero-mean constraint on the free surface, that is
$h_0$, we add the zero-mean constraint on the free surface, that is
which is invariant in the time evolution of Euler's equations.
Let ![]() $\varphi (x,y,t)$ be the velocity potential, which satisfies the Laplace equation in the time-dependent spatial domain
$\varphi (x,y,t)$ be the velocity potential, which satisfies the Laplace equation in the time-dependent spatial domain
subject to the periodic boundary conditions at ![]() $x = \pm {\rm \pi}$ and the Neumann boundary condition at
$x = \pm {\rm \pi}$ and the Neumann boundary condition at ![]() $y = -h_0$. The formulation of the water wave problem is completed by two additional (kinematic and dynamic) conditions at the free surface
$y = -h_0$. The formulation of the water wave problem is completed by two additional (kinematic and dynamic) conditions at the free surface ![]() $y = \eta (x,t)$
$y = \eta (x,t)$
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \eta_t + \varphi_x \eta_x - \varphi_y = 0, \\ \varphi_t + \tfrac{1}{2} (\varphi_x)^2 + \tfrac{1}{2} (\varphi_y)^2 + \eta = 0, \end{gathered}\right\}\quad {\rm at}\ y = \eta(x,t), \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \eta_t + \varphi_x \eta_x - \varphi_y = 0, \\ \varphi_t + \tfrac{1}{2} (\varphi_x)^2 + \tfrac{1}{2} (\varphi_y)^2 + \eta = 0, \end{gathered}\right\}\quad {\rm at}\ y = \eta(x,t), \end{equation}
where the gravitational constant ![]() $g$ is set to unity for convenience.
$g$ is set to unity for convenience.
The method of conformal transformations is used to map the spatial domain ![]() $D_{\eta }$ to the flat domain
$D_{\eta }$ to the flat domain
where ![]() $h$ may be different from
$h$ may be different from ![]() $h_0$. The transformation is based on the conformal mapping
$h_0$. The transformation is based on the conformal mapping ![]() $x + \textrm {i}y = z(u+\textrm {i}v,t)$, where
$x + \textrm {i}y = z(u+\textrm {i}v,t)$, where ![]() $w := u + \textrm {i}v$ is a new complex variable and
$w := u + \textrm {i}v$ is a new complex variable and ![]() $z \in C^{\omega }(\mathcal {D})$ is a holomorphic function, the real and imaginary parts of which satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann equations
$z \in C^{\omega }(\mathcal {D})$ is a holomorphic function, the real and imaginary parts of which satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann equations
To preserve the flat bottom ![]() $y = -h_0$ at
$y = -h_0$ at ![]() $v = -h$, one needs to add the Neumann condition
$v = -h$, one needs to add the Neumann condition ![]() $\partial _v x |_{v = -h} = 0$, which ensures that
$\partial _v x |_{v = -h} = 0$, which ensures that ![]() $y(u,-h,t) = -h_0$ is
$y(u,-h,t) = -h_0$ is ![]() $u$-independent. In addition, we require
$u$-independent. In addition, we require ![]() $x - u$ and
$x - u$ and ![]() $y - v$ be
$y - v$ be ![]() $2{\rm \pi}$-periodic functions of
$2{\rm \pi}$-periodic functions of ![]() $u \in \mathbb {T} := \mathbb {R} \backslash (2 {\rm \pi}\mathbb {Z})$ to ensure that
$u \in \mathbb {T} := \mathbb {R} \backslash (2 {\rm \pi}\mathbb {Z})$ to ensure that ![]() $x({\rm \pi},v,t) - x(-{\rm \pi},v,t) = 2{\rm \pi}$.
$x({\rm \pi},v,t) - x(-{\rm \pi},v,t) = 2{\rm \pi}$.
Abusing notations we refer to ![]() $x = x(u,t)$ and
$x = x(u,t)$ and ![]() $y = \eta (u,t)$ at the top boundary of
$y = \eta (u,t)$ at the top boundary of ![]() $\mathcal {D}$
$\mathcal {D}$
Similarly, we abuse notations for the velocity potential ![]() $\varphi (u,v,t)$ and define
$\varphi (u,v,t)$ and define
on the flat top boundary of ![]() $\mathcal {D}$. Since the conformal transformation preserves the periodic boundary conditions and the zero vertical velocity condition at
$\mathcal {D}$. Since the conformal transformation preserves the periodic boundary conditions and the zero vertical velocity condition at ![]() $v = -h$, the Laplace equation can be solved with the following Fourier series:
$v = -h$, the Laplace equation can be solved with the following Fourier series:
 \begin{equation} \varphi(u,v,t) = \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{\xi}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} \frac{\cosh (n (v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \varphi(u,v,t) = \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{\xi}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} \frac{\cosh (n (v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}, \end{equation}
where ![]() $\hat {\xi }_n(t)$ is the Fourier coefficient for
$\hat {\xi }_n(t)$ is the Fourier coefficient for ![]() $\xi (u,t) = \varphi (u,v=0,t)$. Similarly, we obtain
$\xi (u,t) = \varphi (u,v=0,t)$. Similarly, we obtain
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} x(u,v,t) = u + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{x}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} \frac{\cosh (n(v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}, \\ y(u,v,t) = v + \hat{\eta}_0 + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{x}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} {\rm i} \frac{\sinh (n(v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} x(u,v,t) = u + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{x}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} \frac{\cosh (n(v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}, \\ y(u,v,t) = v + \hat{\eta}_0 + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} \hat{x}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} {\rm i} \frac{\sinh (n(v + h))}{\cosh(n h)}. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
It follows from ![]() $y(u,-h,t) = -h_0$ that
$y(u,-h,t) = -h_0$ that ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0 = h - h_0$. If
$\hat {\eta }_0 = h - h_0$. If ![]() $\hat {\eta }_0(t) = ({1}/{2{\rm \pi} }) \oint \eta (u,t) du$ depends on time
$\hat {\eta }_0(t) = ({1}/{2{\rm \pi} }) \oint \eta (u,t) du$ depends on time ![]() $t$, so does
$t$, so does ![]() $h(t)$ which satisfies
$h(t)$ which satisfies ![]() $\partial _t \eta (u,-h,t) - h'(t) \partial _v \eta (u,-h,t)= 0$ for all
$\partial _t \eta (u,-h,t) - h'(t) \partial _v \eta (u,-h,t)= 0$ for all ![]() $u \in \mathbb {T}$.
$u \in \mathbb {T}$.
Reducing the Fourier series for ![]() $x(u,v,t)$ and
$x(u,v,t)$ and ![]() $y(u,v,t)$ on
$y(u,v,t)$ on ![]() $v = 0$ yields
$v = 0$ yields
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} x(u,t) = u + \hat{x}_0(t) + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z} \backslash \{0\}} \hat{\eta}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} (-{\rm i}) \coth(nh), \\ \eta(u,t) = \hat{\eta}_0(t) + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z} \backslash \{0\}} \hat{\eta}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u}, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} x(u,t) = u + \hat{x}_0(t) + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z} \backslash \{0\}} \hat{\eta}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u} (-{\rm i}) \coth(nh), \\ \eta(u,t) = \hat{\eta}_0(t) + \sum_{n \in \mathbb{Z} \backslash \{0\}} \hat{\eta}_n(t) \,{\rm e}^{{\rm i} n u}, \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
with the correspondence ![]() $\hat {\eta }_n(t) = \textrm {i} \tanh (nh) \hat {x}_n(t)$ for
$\hat {\eta }_n(t) = \textrm {i} \tanh (nh) \hat {x}_n(t)$ for ![]() $n \in \mathbb {Z} \backslash \{0\}$.
$n \in \mathbb {Z} \backslash \{0\}$.
Let us introduce the non-local operator ![]() $T_h$ with the Fourier symbol given by
$T_h$ with the Fourier symbol given by
so that ![]() $\eta = \hat {\eta }_0 + T_h (x - u)$. The inverse of
$\eta = \hat {\eta }_0 + T_h (x - u)$. The inverse of ![]() $T_h$ is only defined on the zero-mean functions with the Fourier symbol given by
$T_h$ is only defined on the zero-mean functions with the Fourier symbol given by
Inverting ![]() $\eta = \hat {\eta }_0 + T_h (x - u)$ yields
$\eta = \hat {\eta }_0 + T_h (x - u)$ yields ![]() $x = u + \hat {x}_0 + T_h^{-1} \eta$ and
$x = u + \hat {x}_0 + T_h^{-1} \eta$ and
where ![]() $K_h := T_h^{-1} \partial _u$ is a linear, self-adjoint, positive operator on
$K_h := T_h^{-1} \partial _u$ is a linear, self-adjoint, positive operator on ![]() $L^2(\mathbb {T})$. We set
$L^2(\mathbb {T})$. We set ![]() $\hat {x}_0 = 0$ in
$\hat {x}_0 = 0$ in ![]() $x = u + \hat {x}_0 + T_h^{-1} \eta$ without loss of generality.
$x = u + \hat {x}_0 + T_h^{-1} \eta$ without loss of generality.
The equations of motion can be derived from the following Lagrangian (see Dyachenko et al. (Reference Dyachenko, Kuznetsov, Spector and Zakharov1996) and Dyachenko et al. (Reference Dyachenko, Lushnikov and Korotkevich2016), Appendix A for ![]() $h = \infty$):
$h = \infty$):
 \begin{align} \mathcal{L}(\xi,\eta,x) &:= \oint \xi(\eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t) \,{\rm d} u + \tfrac{1}{2} \oint \xi T_h \xi_u \,{\rm d} u - \tfrac{1}{2} \oint \eta^2 x_u \,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &\quad +\oint f (\eta - T_h(x-u)) \,{\rm d} u, \end{align}
\begin{align} \mathcal{L}(\xi,\eta,x) &:= \oint \xi(\eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t) \,{\rm d} u + \tfrac{1}{2} \oint \xi T_h \xi_u \,{\rm d} u - \tfrac{1}{2} \oint \eta^2 x_u \,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &\quad +\oint f (\eta - T_h(x-u)) \,{\rm d} u, \end{align}
where ![]() $f$ is the Lagrange multiplier satisfying
$f$ is the Lagrange multiplier satisfying ![]() $\oint f \,\textrm {d} u = 0$. Variation of
$\oint f \,\textrm {d} u = 0$. Variation of ![]() $\mathcal {L}$ in
$\mathcal {L}$ in ![]() $\xi$,
$\xi$, ![]() $\eta$ and
$\eta$ and ![]() $x$ yields the system of equations
$x$ yields the system of equations
 \begin{equation}
\left. \begin{array}{@{}l} \eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t + T_h
\xi_u = 0, \\ -\xi_t x_u + \xi_u x_t - \eta x_u + f = 0, \\
\xi_t \eta_u - \xi_u \eta_t + \eta \eta_u + T_h f = 0,
\end{array}\right\}
\end{equation}
\begin{equation}
\left. \begin{array}{@{}l} \eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t + T_h
\xi_u = 0, \\ -\xi_t x_u + \xi_u x_t - \eta x_u + f = 0, \\
\xi_t \eta_u - \xi_u \eta_t + \eta \eta_u + T_h f = 0,
\end{array}\right\}
\end{equation}
with the additional constraint due to the reduction ![]() $h = h_0 + ({1}/{2{\rm \pi} }) \oint \eta \,\textrm {d} u$
$h = h_0 + ({1}/{2{\rm \pi} }) \oint \eta \,\textrm {d} u$
Taking mean values in each equation of system (A15) and integrating by parts yields three conserved quantities
where the constraint ![]() $M_1(\eta ) = 0$ follows from the zero-mean constraint (A1) in physical coordinates. We express
$M_1(\eta ) = 0$ follows from the zero-mean constraint (A1) in physical coordinates. We express ![]() $f$ from the second equation of system (A15), substitute it into the third equation and invert
$f$ from the second equation of system (A15), substitute it into the third equation and invert ![]() $T_h$ on the periodic functions with zero mean. This transforms the system (A15) to the following system of two equations for
$T_h$ on the periodic functions with zero mean. This transforms the system (A15) to the following system of two equations for ![]() $\xi$ and
$\xi$ and ![]() $\eta$:
$\eta$:
The constraint (A16) is rewritten in the equivalent form
The conserved energy of system (A20) is given by
To derive (A22), we multiply the first equation of system (A20) by ![]() $\xi _t$ and the second equation by
$\xi _t$ and the second equation by ![]() $\eta _t$, integrate over the period and subtract one equation from another. After integration by parts, we get
$\eta _t$, integrate over the period and subtract one equation from another. After integration by parts, we get ![]() $({\textrm {d}}/{\textrm {d} t}) H(\xi,\eta ) = 0$ if and only if
$({\textrm {d}}/{\textrm {d} t}) H(\xi,\eta ) = 0$ if and only if
 \begin{align} & -\tfrac{1}{2} h'(t) \oint \xi (\partial_h T_h) \xi_u \,{\rm d} u - h'(t) \oint \eta \eta_u (\partial_h T_h^{-1}) \eta \,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &\quad - \oint (\xi_t \eta_u - \xi_u \eta_t ) (x_t - T_h^{-1} \eta_t) \,{\rm d} u = 0. \end{align}
\begin{align} & -\tfrac{1}{2} h'(t) \oint \xi (\partial_h T_h) \xi_u \,{\rm d} u - h'(t) \oint \eta \eta_u (\partial_h T_h^{-1}) \eta \,{\rm d} u \nonumber\\ &\quad - \oint (\xi_t \eta_u - \xi_u \eta_t ) (x_t - T_h^{-1} \eta_t) \,{\rm d} u = 0. \end{align}
Since ![]() $x_t - T_h^{-1} \eta _t = h'(t) (\partial _h T_h^{-1}) \eta$,
$x_t - T_h^{-1} \eta _t = h'(t) (\partial _h T_h^{-1}) \eta$, ![]() $\partial _h T_h^{-1} = - T_h^{-1} (\partial _h T_h) T_h^{-1}$ and
$\partial _h T_h^{-1} = - T_h^{-1} (\partial _h T_h) T_h^{-1}$ and ![]() $T_h^{-1}$ is skew–adjoint, the last constraint is identical to the constraint (A21) for every
$T_h^{-1}$ is skew–adjoint, the last constraint is identical to the constraint (A21) for every ![]() $h'(t)$. This proves the conservation of
$h'(t)$. This proves the conservation of ![]() $H(\xi,\eta )$.
$H(\xi,\eta )$.
The conserved quantities (A17), (A18), (A19) and (A22) coincide with the conserved quantities for Euler's equation in physical coordinates, see Benjamin & Olver (Reference Benjamin and Olver1982) and Dyachenko et al. (Reference Dyachenko, Kuznetsov, Spector and Zakharov1996) for ![]() $h = \infty$.
$h = \infty$.
In order to introduce the scalar model (1.1), we rewrite (A20) in the reference frame moving with the wave speed ![]() $c$
$c$
where ![]() $u$ now stands for
$u$ now stands for ![]() $u - ct$ and we have used the chain rule with
$u - ct$ and we have used the chain rule with
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \xi_t \to \xi_t - c \xi_u, \\ \eta_t \to \eta_t - c \eta_u, \\ x_t \to x_t + c - c x_u. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered} \xi_t \to \xi_t - c \xi_u, \\ \eta_t \to \eta_t - c \eta_u, \\ x_t \to x_t + c - c x_u. \end{gathered}\right\} \end{equation}We introduce a change of variables by
after which the system (A24) can be rewritten in the form
 \begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered}
\eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t + T_h \zeta_u = 0, \\ \zeta_t x_u -
\zeta_u x_t + \eta (1 + K_h \eta) - c \zeta_u + c x_t - c^2
K_h \eta \\ \quad +\, T_h^{-1} ( \zeta_t \eta_u - \zeta_u
\eta_t + \eta \eta_u + c \eta_u x_t - c \eta_t K_h \eta ) =
0. \end{gathered}\right\}
\end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left.\begin{gathered}
\eta_t x_u - \eta_u x_t + T_h \zeta_u = 0, \\ \zeta_t x_u -
\zeta_u x_t + \eta (1 + K_h \eta) - c \zeta_u + c x_t - c^2
K_h \eta \\ \quad +\, T_h^{-1} ( \zeta_t \eta_u - \zeta_u
\eta_t + \eta \eta_u + c \eta_u x_t - c \eta_t K_h \eta ) =
0. \end{gathered}\right\}
\end{equation}
Substituting ![]() $- c \zeta _u = c T_h^{-1} (\eta _t x_u - \eta _u x_t)$ to the second equation of system (A27) and taking the derivative of
$- c \zeta _u = c T_h^{-1} (\eta _t x_u - \eta _u x_t)$ to the second equation of system (A27) and taking the derivative of ![]() $x = u + T_h^{-1} \eta$ in
$x = u + T_h^{-1} \eta$ in ![]() $t$ yields
$t$ yields
 \begin{align} & \zeta_t x_u - \zeta_u x_t + T_h^{-1} (\zeta_t \eta_u - \zeta_u \eta_t ) + h'(t) (\partial_h T_h^{-1}) \eta \nonumber\\ &\quad + 2 c T_h^{-1} \eta_t - c^2 K_h \eta + \eta (1 + K_h \eta) + \tfrac{1}{2} K_h \eta^2 = 0. \end{align}
\begin{align} & \zeta_t x_u - \zeta_u x_t + T_h^{-1} (\zeta_t \eta_u - \zeta_u \eta_t ) + h'(t) (\partial_h T_h^{-1}) \eta \nonumber\\ &\quad + 2 c T_h^{-1} \eta_t - c^2 K_h \eta + \eta (1 + K_h \eta) + \tfrac{1}{2} K_h \eta^2 = 0. \end{align}
The scalar model (1.1) follows by ignoring the constraint (A21) and the first equation of system (A27) and by setting ![]() $\zeta \equiv 0$ and
$\zeta \equiv 0$ and ![]() $h'(t) \equiv 0$ in (A28). Babenko's equation (1.8), which is the exact equation for travelling waves, see Babenko (Reference Babenko1987), corresponds to the time-independent solutions of (A27) and (A28) with
$h'(t) \equiv 0$ in (A28). Babenko's equation (1.8), which is the exact equation for travelling waves, see Babenko (Reference Babenko1987), corresponds to the time-independent solutions of (A27) and (A28) with ![]() $\zeta \equiv 0$ and
$\zeta \equiv 0$ and ![]() $h'(t) \equiv 0$ since
$h'(t) \equiv 0$ since ![]() $u$ in (1.1) stands for
$u$ in (1.1) stands for ![]() $u - ct$.
$u - ct$.
Appendix B. Introducing the local model
One popular model for fluid motion is the intermediate long-wave (ILW) equation written in the form
where ![]() $\mathcal {K}_h$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
$\mathcal {K}_h$ is defined by the Fourier symbol
In comparison with (1.3), we have the correspondence
The ILW equation (B1) is integrable by inverse scattering and many results on well posedness and the dynamics of nonlinear waves have been obtained for this fluid model, see review in Saut (Reference Saut2019). In the shallow water limit ![]() $h \to 0$, the scaling transformation
$h \to 0$, the scaling transformation
recovers formally the Korteweg–de Vries (KdV) equation
due to the asymptotic expansion
For completeness, in the deep water limit ![]() $h \to \infty$, the ILW equation (B1) becomes the Benjamin–Ono (BO) equation
$h \to \infty$, the ILW equation (B1) becomes the Benjamin–Ono (BO) equation
where ![]() $\mathcal {H}$ is the periodic Hilbert transform defined by (1.10). Both the KdV and BO equations are also integrable by inverse scattering.
$\mathcal {H}$ is the periodic Hilbert transform defined by (1.10). Both the KdV and BO equations are also integrable by inverse scattering.
To obtain the local evolution equation (1.11) from the non-local model (1.1), we replace ![]() $K_h$ given by (1.3) with
$K_h$ given by (1.3) with
The difference between ![]() $\tilde {K}_h$ and
$\tilde {K}_h$ and ![]() $K_h$ appears in the local term
$K_h$ appears in the local term ![]() $1/h$. It is removed from the mean term in the definition of
$1/h$. It is removed from the mean term in the definition of ![]() $K_h$ and from all Fourier modes in the definition of
$K_h$ and from all Fourier modes in the definition of ![]() $\tilde {K}_h$. Since
$\tilde {K}_h$. Since ![]() $K_h = T_h^{-1} \partial _u$, we can similarly define
$K_h = T_h^{-1} \partial _u$, we can similarly define ![]() $\tilde {K}_h = \tilde {T}_h^{-1} \partial _u$ and expand asymptotically as
$\tilde {K}_h = \tilde {T}_h^{-1} \partial _u$ and expand asymptotically as ![]() $h \to 0$
$h \to 0$
By using the scaling transformation
we obtain the formal limit of the non-local model (1.1) as ![]() $h \to 0$ in the form
$h \to 0$ in the form
Expanding the derivatives, changing the sign and removing the tilde notations yields the local model (1.11).