Cover: FIG. 3(a) SEM image of Ni foam. [X. Wang, G. Wang, G. Zhai, and H. Wang: Preparation and electrochemical evaluation of NiO nanoplatelet-based materials for lithium storage. p. 1393].
Articles
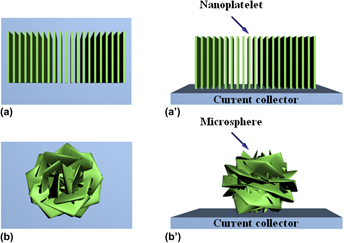
Preparation and electrochemical evaluation of NiO nanoplatelet-based materials for lithium storage
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2014, pp. 1393-1400
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pristine graphene quantum dots for detection of copper ions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. 1401-1407
-
- Article
- Export citation
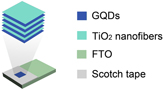
N-doped graphene quantum dots-functionalized titanium dioxide nanofibers and their highly efficient photocurrent response
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. 1408-1416
-
- Article
- Export citation
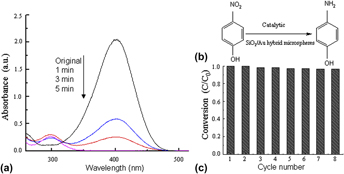
Facile synthesis of the SiO2/Au hybrid microspheres for excellent catalytic performance
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2014, pp. 1417-1423
-
- Article
- Export citation
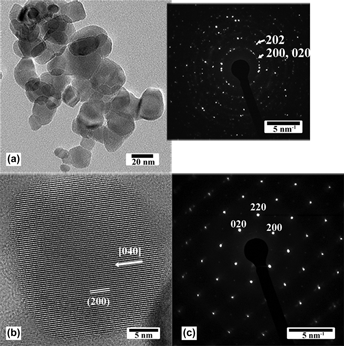
Synthesis of tungsten oxide nanoparticles using a hydrothermal method at ambient pressure
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2014, pp. 1424-1430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Solvothermal synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties of pyramidal Ni superstructures
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2014, pp. 1431-1439
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural evolution of MgAl2O4 oxide-dispersion-strengthened alloy by mechanical milling and hot isostatic pressing
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2014, pp. 1440-1447
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of high magnetic field on austenite formation and grain size in a hypereutectoid carbon steel
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. 1448-1455
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ elevated temperature transmission electron microscopy of sensitized aluminum–magnesium alloy treated by ultrasonic impact treatment
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2014, pp. 1456-1462
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the atomic interdiffusion in Mg–{Ce, Nd, Zn} and Zn–{Ce, Nd} binary systems
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. 1463-1479
-
- Article
- Export citation
Densification and deformation studies on powder metallurgy Al–TiO2–Gr composite during cold upsetting
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2014, pp. 1480-1487
-
- Article
- Export citation
Front Cover (OFC, IFC) and matter
JMR volume 29 issue 13 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Back Cover (OBC, IBC) and matter
JMR volume 29 issue 13 Cover and Back matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2014, pp. b1-b5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation