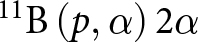Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
Open access
Contents
Corrigendum
Status and perspectives of the FUSION INFN project for the study and optimization of the 11B(p, α)2α nuclear fusion reaction for Inertial Confinement applications – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2025, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research Article
Contaminant-free alpha particles signature from laser-driven proton-boron fusion plasma using Thomson parabola spectrometer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2025, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Real-time wavelength calibration and multi-technique plasma diagnostics in discharge capillary
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2025, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corrigendum
Challenges of preliminary investigation of high repetition rate experiments enabling new paths on high energy density physics – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2025, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research Article
Challenges of preliminary investigation of high repetition rate experiments enabling new paths on high energy density physics
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2025, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perspectives
Status and perspectives of the FUSION INFN project for the study and optimization of the
 $^{11}\text{B}(\text{p},\alpha)2\alpha$ nuclear fusion reaction for Inertial Confinement applications
$^{11}\text{B}(\text{p},\alpha)2\alpha$ nuclear fusion reaction for Inertial Confinement applications
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2025, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research Article
Smoothing of transverse nonuniformities at the critical density in laser interaction with nonuniform plasmas
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2025, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Active-controlled cascaded proton acceleration using a solenoid driven by picosecond laser pulse
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2025, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A mechanism that could stop the acceleration process within a collisionless shock
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2025, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Forward ion acceleration by laser-driven collisionless filamentary shocks in underdense plasmas
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Proton–boron fusion in a hydrogen-doped-boron target
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical analysis of X-ray multilayer Fresnel zone plates with high aspect ratios
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hot electron emission characteristics from thin metal foil targets irradiated by terawatt laser
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flux and estimated spectra from a low-intensity laser-driven X-ray source
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research Article
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modeling of a Liquid Leaf Target TNSA Experiment Using Particle-In-Cell Simulations and Deep Learning
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis of the p-11B Fusion Scenario with Compensation of the Transfer of Kinetic Energy of Protons and Alpha Particles to the Gas Medium by the Electric Field
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of Energetic Protons Generated in the ShenGuang-II UP Petawatt Laser Interactions with Foil Targets
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-Sensitivity Thomson Spectrometry in Experiments of Laser-Driven Low-Rate NeutronLess Fusion Reactions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation